Java 反序列化工具 gadgetinspector 初窥
作者:Longofo@知道创宇404实验室
时间:2019年9月4日
起因
一开始是听@Badcode师傅说的这个工具,在Black Hat 2018的一个议题提出来的。这是一个基于字节码静态分析的、利用已知技巧自动查找从source到sink的反序列化利用链工具。看了几遍作者在Black Hat上的演讲视频与PPT,想从作者的演讲与PPT中获取更多关于这个工具的原理性的东西,可是有些地方真的很费解。不过作者开源了这个工具,但没有给出详细的说明文档,对这个工具的分析文章也很少,看到一篇平安集团对这个工具的分析,从文中描述来看,他们对这个工具应该有一定的认识并做了一些改进,但是在文章中对某些细节没有做过多的阐释。后面尝试了调试这个工具,大致理清了这个工具的工作原理,下面是对这个工具的分析过程,以及对未来工作与改进的设想。
关于这个工具
- 这个工具不是用来寻找漏洞,而是利用已知的source->...->sink链或其相似特征发现分支利用链或新的利用链。
- 这个工具是在整个应用的classpath中寻找利用链。
- 这个工具进行了一些合理的预估风险判断(污点判断、污点传递等)。
- 这个工具会产生误报不是漏报(其实这里还是会漏报,这是作者使用的策略决定的,在后面的分析中可以看到)。
- 这个工具是基于字节码分析的,对于Java应用来说,很多时候我们并没有源码,而只有War包、Jar包或class文件。
- 这个工具不会生成能直接利用的Payload,具体的利用构造还需要人工参与。
序列化与反序列化
序列化(Serialization)是将对象的状态信息转化为可以存储或者传输形式的过程,转化后的信息可以存储在磁盘上,在网络传输过程中,可以是字节、XML、JSON等格式;而将字节、XML、JSON等格式的信息还原成对象这个相反的过程称为反序列化。
在JAVA中,对象的序列化和反序列化被广泛的应用到RMI(远程方法调用)及网络传输中。
Java中的序列化与反序列化库
- JDK(ObjectInputStream)
- XStream(XML,JSON)
- Jackson(XML,JSON)
- Genson(JSON)
- JSON-IO(JSON)
- FlexSON(JSON)
- Fastjson(JSON)
- ...
不同的反序列化库在反序列化不同的类时有不同的行为、被反序列化类的不同"魔术方法"会被自动调用,这些被自动调用的方法就能够作为反序列化的入口点(source)。如果这些被自动调用的方法又调用了其他子方法,那么在调用链中某一个子方法也可以作为source,就相当于已知了调用链的前部分,从某个子方法开始寻找不同的分支。通过方法的层层调用,可能到达某些危险的方法(sink)。
- ObjectInputStream
例如某个类实现了Serializable接口,ObjectInputStream.readobject在反序列化类得到其对象时会自动查找这个类的readObject、readResolve等方法并调用。
例如某个类实现了Externalizable接口,ObjectInputStream.readobject在反序列化类得到其对象时会自动查找这个类的readExternal等方法并调用。
- Jackson
ObjectMapper.readValue在反序列化类得到其对象时,会自动查找反序列化类的无参构造方法、包含一个基础类型参数的构造方法、属性的setter、属性的getter等方法并调用。
- ...
在后面的分析中,都使用JDK自带的ObjectInputStream作为样例。
控制数据类型=>控制代码
作者说,在反序列化漏洞中,如果控制了数据类型,我们就控制了代码。这是什么意思呢?按我的理解,写了下面的一个例子:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 |
public class TestDeserialization { interface Animal { public void eat(); } public static class Cat implements Animal,Serializable { @Override public void eat() { System.out.println("cat eat fish"); } } public static class Dog implements Animal,Serializable { @Override public void eat() { try { Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("dog eat bone"); } } public static class Person implements Serializable { private Animal pet; public Person(Animal pet){ this.pet = pet; } private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream stream) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { pet = (Animal) stream.readObject(); pet.eat(); } } public static void GeneratePayload(Object instance, String file) throws Exception { //将构造好的payload序列化后写入文件中 File f = new File(file); ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(f)); out.writeObject(instance); out.flush(); out.close(); } public static void payloadTest(String file) throws Exception { //读取写入的payload,并进行反序列化 ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(file)); Object obj = in.readObject(); System.out.println(obj); in.close(); } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Animal animal = new Dog(); Person person = new Person(animal); GeneratePayload(person,"test.ser"); payloadTest("test.ser"); // Animal animal = new Cat(); // Person person = new Person(animal); // GeneratePayload(person,"test.ser"); // payloadTest("test.ser"); } } |
为了方便我把所有类写在一个类中进行测试。在Person类中,有一个Animal类的属性pet,它是Cat和Dog的接口。在序列化时,我们能够控制Person的pet具体是Cat对象或者Dog对象,因此在反序列化时,在readObject中pet.eat()具体的走向就不一样了。如果是pet是Cat类对象,就不会走到执行有害代码Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");这一步,但是如果pet是Dog类的对象,就会走到有害代码。
即使有时候类属性在声明时已经为它赋值了某个具体的对象,但是在Java中通过反射等方式依然能修改。如下:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 |
public class TestDeserialization { interface Animal { public void eat(); } public static class Cat implements Animal, Serializable { @Override public void eat() { System.out.println("cat eat fish"); } } public static class Dog implements Animal, Serializable { @Override public void eat() { try { Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("dog eat bone"); } } public static class Person implements Serializable { private Animal pet = new Cat(); private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream stream) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { pet = (Animal) stream.readObject(); pet.eat(); } } public static void GeneratePayload(Object instance, String file) throws Exception { //将构造好的payload序列化后写入文件中 File f = new File(file); ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(f)); out.writeObject(instance); out.flush(); out.close(); } public static void payloadTest(String file) throws Exception { //读取写入的payload,并进行反序列化 ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(file)); Object obj = in.readObject(); System.out.println(obj); in.close(); } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Animal animal = new Dog(); Person person = new Person(); //通过反射修改私有属性 Field field = person.getClass().getDeclaredField("pet"); field.setAccessible(true); field.set(person, animal); GeneratePayload(person, "test.ser"); payloadTest("test.ser"); } } |
在Person类中,不能通过构造器或setter方法或其他方式对pet赋值,属性在声明时已经被定义为Cat类的对象,但是通过反射能将pet修改为Dog类的对象,因此在反序列化时依然会走到有害代码处。
这只是我自己对作者"控制了数据类型,就控制了代码"的理解,在Java反序列化漏洞中,很多时候是利用到了Java的多态特性来控制代码走向最后达到恶意执行目的。
魔术方法
在上面的例子中,能看到在反序列化时没有调用Person的readobject方法,它是ObjectInputStream在反序列化对象时自动调用的。作者将在反序列化中会自动调用的方法称为"魔术方法"。
使用ObjectInputStream反序列化时几个常见的魔术方法:
- Object.readObject()
- Object.readResolve()
- Object.finalize()
- ...
一些可序列化的JDK类实现了上面这些方法并且还自动调用了其他方法(可以作为已知的入口点):
- HashMap
- Object.hashCode()
- Object.equals()
- PriorityQueue
- Comparator.compare()
- Comparable.CompareTo()
- ...
一些sink:
- Runtime.exec(),这种最为简单直接,即直接在目标环境中执行命令
- Method.invoke(),这种需要适当地选择方法和参数,通过反射执行Java方法
- RMI/JNDI/JRMP等,通过引用远程对象,间接实现任意代码执行的效果
- ...
作者给出了一个从Magic Methods(source)->Gadget Chains->Runtime.exec(sink)的例子:
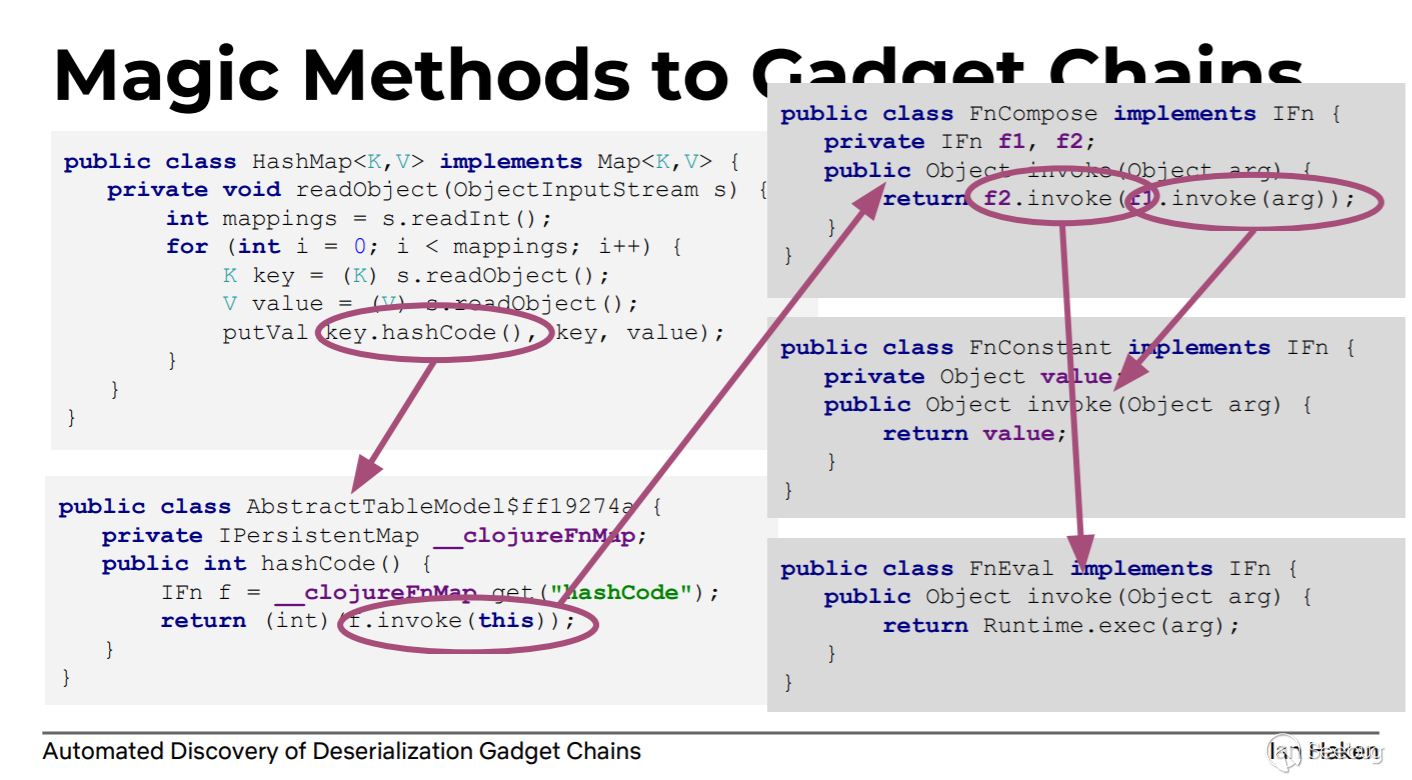
上面的HashMap实现了readObject这个"魔术方法",并且调用了hashCode方法。某些类为了比较对象之间是否相等会实现equals方法(一般是equals和hashCode方法同时实现)。从图中可以看到AbstractTableModel$ff19274a正好实现了hashCode方法,其中又调用了f.invoke方法,f是IFn对象,并且f能通过属性__clojureFnMap获取到。IFn是一个接口,上面说到,如果控制了数据类型,就控制了代码走向。所以如果我们在序列化时,在__clojureFnMap放置IFn接口的实现类FnCompose的一个对象,那么就能控制f.invoke走FnCompose.invoke方法,接着控制FnCompose.invoke中的f1、f2为FnConstant就能到达FnEval.invoke了(关于AbstractTableModel$ff19274a.hashcode中的f.invoke具体选择IFn的哪个实现类,根据后面对这个工具的测试以及对决策原理的分析,广度优先会选择短的路径,也就是选择了FnEval.invoke,所以这也是为什么要人为参与,在后面的样例分析中也可以看到)。
有了这条链,只需要找到触发这个链的漏洞点就行了。Payload使用JSON格式表示如下:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
{ "@class":"java.util.HashMap", "members":[ 2, { "@class":"AbstractTableModel$ff19274a", "__clojureFnMap":{ "hashcode":{ "@class":"FnCompose", "f1":{"@class","FnConstant",value:"calc"}, "f2":{"@class":"FnEval"} } } } ] } |
gadgetinspector工作流程
如作者所说,正好使用了五个步骤:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 |
// 枚举全部类以及类的所有方法 if (!Files.exists(Paths.get("classes.dat")) || !Files.exists(Paths.get("methods.dat")) || !Files.exists(Paths.get("inheritanceMap.dat"))) { LOGGER.info("Running method discovery..."); MethodDiscovery methodDiscovery = new MethodDiscovery(); methodDiscovery.discover(classResourceEnumerator); methodDiscovery.save(); } //生成passthrough数据流 if (!Files.exists(Paths.get("passthrough.dat"))) { LOGGER.info("Analyzing methods for passthrough dataflow..."); PassthroughDiscovery passthroughDiscovery = new PassthroughDiscovery(); passthroughDiscovery.discover(classResourceEnumerator, config); passthroughDiscovery.save(); } //生成passthrough调用图 if (!Files.exists(Paths.get("callgraph.dat"))) { LOGGER.info("Analyzing methods in order to build a call graph..."); CallGraphDiscovery callGraphDiscovery = new CallGraphDiscovery(); callGraphDiscovery.discover(classResourceEnumerator, config); callGraphDiscovery.save(); } //搜索可用的source if (!Files.exists(Paths.get("sources.dat"))) { LOGGER.info("Discovering gadget chain source methods..."); SourceDiscovery sourceDiscovery = config.getSourceDiscovery(); sourceDiscovery.discover(); sourceDiscovery.save(); } //搜索生成调用链 { LOGGER.info("Searching call graph for gadget chains..."); GadgetChainDiscovery gadgetChainDiscovery = new GadgetChainDiscovery(config); gadgetChainDiscovery.discover(); } |
Step1 枚举全部类以及每个类的所有方法
要进行调用链的搜索,首先得有所有类及所有类方法的相关信息:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 |
public class MethodDiscovery { private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MethodDiscovery.class); private final List<ClassReference> discoveredClasses = new ArrayList<>();//保存所有类信息 private final List<MethodReference> discoveredMethods = new ArrayList<>();//保存所有方法信息 ... ... public void discover(final ClassResourceEnumerator classResourceEnumerator) throws Exception { //classResourceEnumerator.getAllClasses()获取了运行时的所有类(JDK rt.jar)以及要搜索应用中的所有类 for (ClassResourceEnumerator.ClassResource classResource : classResourceEnumerator.getAllClasses()) { try (InputStream in = classResource.getInputStream()) { ClassReader cr = new ClassReader(in); try { cr.accept(new MethodDiscoveryClassVisitor(), ClassReader.EXPAND_FRAMES);//通过ASM框架操作字节码并将类信息保存到this.discoveredClasses,将方法信息保存到discoveredMethods } catch (Exception e) { LOGGER.error("Exception analyzing: " + classResource.getName(), e); } } } } ... ... public void save() throws IOException { DataLoader.saveData(Paths.get("classes.dat"), new ClassReference.Factory(), discoveredClasses);//将类信息保存到classes.dat DataLoader.saveData(Paths.get("methods.dat"), new MethodReference.Factory(), discoveredMethods);//将方法信息保存到methods.dat Map<ClassReference.Handle, ClassReference> classMap = new HashMap<>(); for (ClassReference clazz : discoveredClasses) { classMap.put(clazz.getHandle(), clazz); } InheritanceDeriver.derive(classMap).save();//查找所有继承关系并保存 } } |
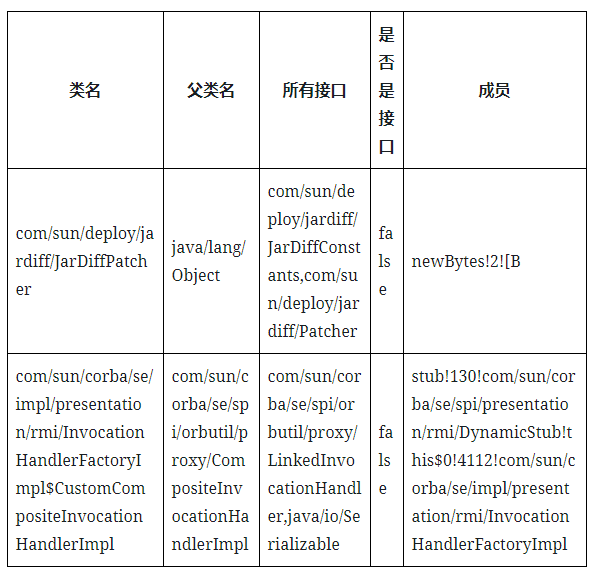
来看下classes.dat、methods.dat分别长什么样子:
- classes.dat
找了两个比较有特征的
第一个类com/sun/deploy/jardiff/JarDiffPatcher:
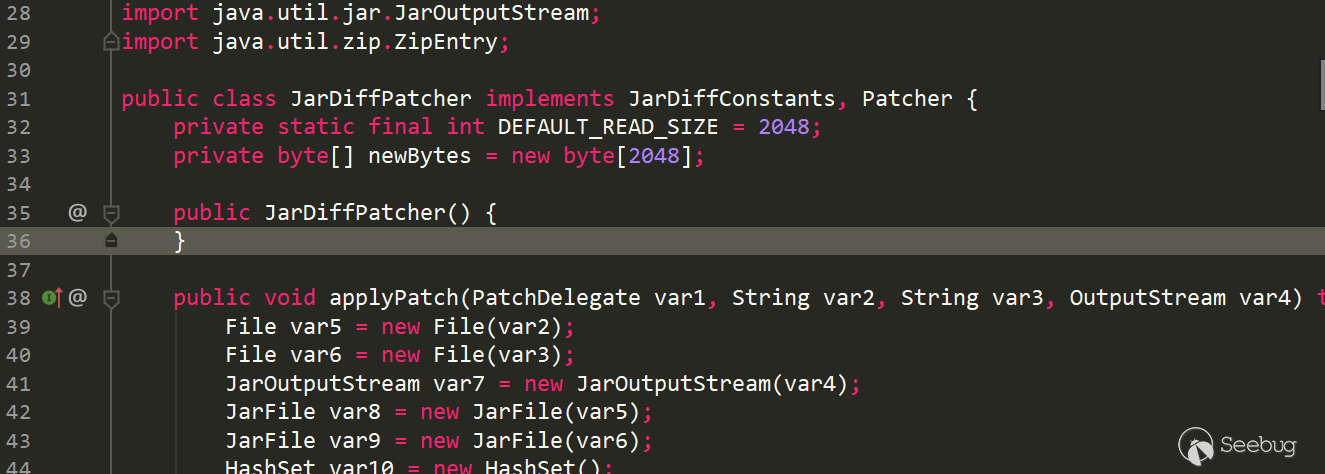
和上面的表格信息对应一下,是吻合的
- 类名:com/sun/deploy/jardiff/JarDiffPatcher
- 父类: java/lang/Object,如果一类没有显式继承其他类,默认隐式继承java/lang/Object,并且java中不允许多继承,所以每个类只有一个父类
- 所有接口:com/sun/deploy/jardiff/JarDiffConstants、com/sun/deploy/jardiff/Patcher
- 是否是接口:false
- 成员:newBytes!2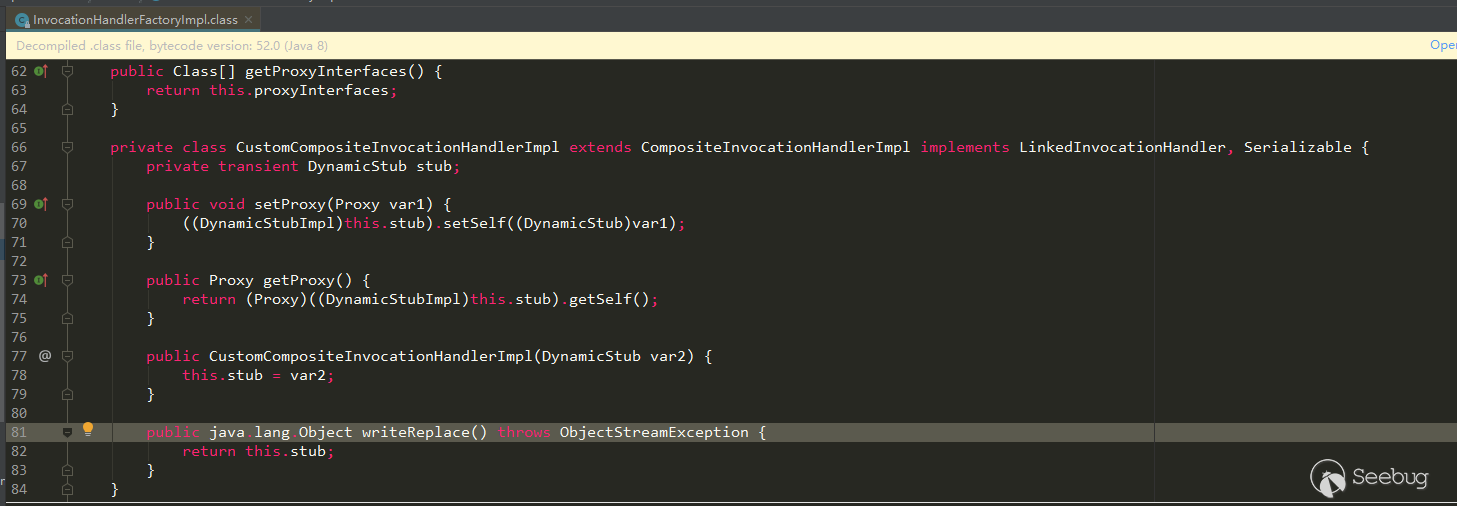
和上面的表格信息对应一下,也是吻合的
- 类名:com/sun/corba/se/impl/presentation/rmi/InvocationHandlerFactoryImpl$CustomCompositeInvocationHandlerImpl,是一个内部类
- 父类: com/sun/corba/se/spi/orbutil/proxy/CompositeInvocationHandlerImpl
- 所有接口:com/sun/corba/se/spi/orbutil/proxy/LinkedInvocationHandler,java/io/Serializable
- 是否是接口:false
- 成员:stub!130!com/sun/corba/se/spi/presentation/rmi/DynamicStub!this$0!4112!com/sun/corba/se/impl/presentation/rmi/InvocationHandlerFactoryImpl,!*!这里可以暂时理解为分割符,有一个成员stub,类型com/sun/corba/se/spi/presentation/rmi/DynamicStub。因为是内部类,所以多了个this成员,这个this指向的是外部类
- methods.dat
同样找几个比较有特征的
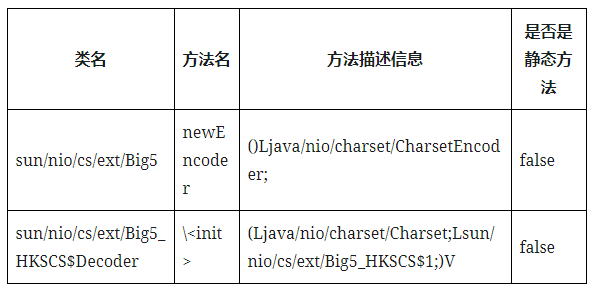
sun/nio/cs/ext/Big5#newEncoder:
- 类名:sun/nio/cs/ext/Big5
- 方法名: newEncoder
- 方法描述信息: ()Ljava/nio/charset/CharsetEncoder; 无参,返回java/nio/charset/CharsetEncoder对象
- 是否是静态方法:false
sun/nio/cs/ext/Big5_HKSCS$Decoder#\<init>:
- 类名:sun/nio/cs/ext/Big5_HKSCS$Decoder
- 方法名:\<init>
- 方法描述信息: (Ljava/nio/charset/Charset;Lsun/nio/cs/ext/Big5_HKSCS1;)V参数1是java/nio/charset/Charset类型,参数2是sun/nio/cs/ext/Big5HKSCS1;)V参数1是java/nio/charset/Charset类型,参数2是sun/nio/cs/ext/Big5HKSCS1类型,返回值void
- 是否是静态方法:false
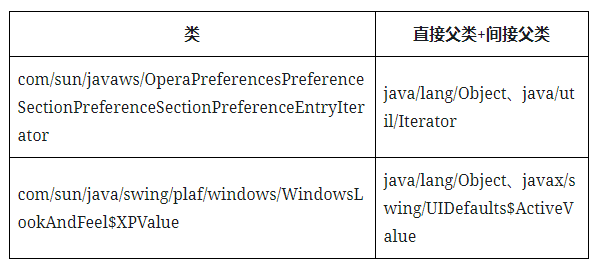
继承关系的生成:
继承关系在后面用来判断一个类是否能被某个库序列化、以及搜索子类方法实现等会用到。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 |
public class InheritanceDeriver { private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(InheritanceDeriver.class); public static InheritanceMap derive(Map<ClassReference.Handle, ClassReference> classMap) { LOGGER.debug("Calculating inheritance for " + (classMap.size()) + " classes..."); Map<ClassReference.Handle, Set<ClassReference.Handle>> implicitInheritance = new HashMap<>(); for (ClassReference classReference : classMap.values()) { if (implicitInheritance.containsKey(classReference.getHandle())) { throw new IllegalStateException("Already derived implicit classes for " + classReference.getName()); } Set<ClassReference.Handle> allParents = new HashSet<>(); getAllParents(classReference, classMap, allParents);//获取当前类的所有父类 implicitInheritance.put(classReference.getHandle(), allParents); } return new InheritanceMap(implicitInheritance); } ... ... private static void getAllParents(ClassReference classReference, Map<ClassReference.Handle, ClassReference> classMap, Set<ClassReference.Handle> allParents) { Set<ClassReference.Handle> parents = new HashSet<>(); if (classReference.getSuperClass() != null) { parents.add(new ClassReference.Handle(classReference.getSuperClass()));//父类 } for (String iface : classReference.getInterfaces()) { parents.add(new ClassReference.Handle(iface));//接口类 } for (ClassReference.Handle immediateParent : parents) { //获取间接父类,以及递归获取间接父类的父类 ClassReference parentClassReference = classMap.get(immediateParent); if (parentClassReference == null) { LOGGER.debug("No class id for " + immediateParent.getName()); continue; } allParents.add(parentClassReference.getHandle()); getAllParents(parentClassReference, classMap, allParents); } } ... ... } |
这一步的结果保存到了inheritanceMap.dat:
Step2 生成passthrough数据流
这里的passthrough数据流指的是每个方法的返回结果与方法参数的关系,这一步生成的数据会在生成passthrough调用图时用到。
以作者给出的demo为例,先从宏观层面判断下:
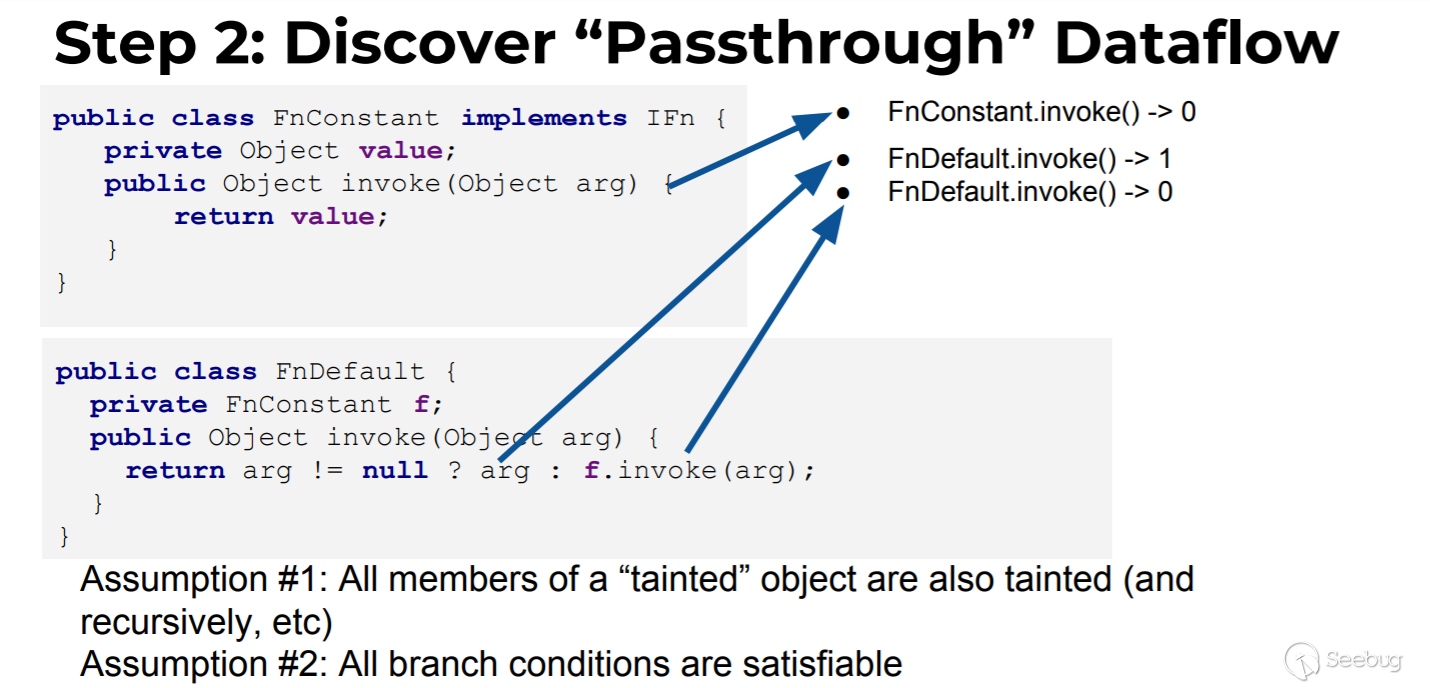
FnConstant.invoke返回值与参数this(参数0,因为序列化时类的所有成员我们都能控制,所以所有成员变量都视为0参)、arg(参数1)的关系:
- 与this的关系:返回了this.value,即与0参有关系
- 与arg的关系:返回值与arg没有任何关系,即与1参没有关系
- 结论就是FnConstant.invoke与参数0有关,表示为FnConstant.invoke()->0
Fndefault.invoke返回值与参数this(参数0)、arg(参数1)的关系:
- 与this的关系:返回条件的第二个分支与this.f有关系,即与0参有关系
- 与arg的关系:返回条件的第一个分支与arg有关系,即与1参有关系
- 结论就是FnConstant.invoke与0参,1参都有关系,表示为Fndefault.invoke()->0、Fndefault.invoke()->1
在这一步中,gadgetinspector是利用ASM来进行方法字节码的分析,主要逻辑是在类PassthroughDiscovery和TaintTrackingMethodVisitor中。特别是TaintTrackingMethodVisitor,它通过标记追踪JVM虚拟机在执行方法时的stack和localvar,并最终得到返回结果是否可以被参数标记污染。
核心实现代码(TaintTrackingMethodVisitor涉及到字节码分析,暂时先不看):
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 |
public class PassthroughDiscovery { private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(PassthroughDiscovery.class); private final Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<MethodReference.Handle>> methodCalls = new HashMap<>(); private Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<Integer>> passthroughDataflow; public void discover(final ClassResourceEnumerator classResourceEnumerator, final GIConfig config) throws IOException { Map<MethodReference.Handle, MethodReference> methodMap = DataLoader.loadMethods();//load之前保存的methods.dat Map<ClassReference.Handle, ClassReference> classMap = DataLoader.loadClasses();//load之前保存的classes.dat InheritanceMap inheritanceMap = InheritanceMap.load();//load之前保存的inheritanceMap.dat Map<String, ClassResourceEnumerator.ClassResource> classResourceByName = discoverMethodCalls(classResourceEnumerator);//查找一个方法中包含的子方法 List<MethodReference.Handle> sortedMethods = topologicallySortMethodCalls();//对所有方法构成的图执行逆拓扑排序 passthroughDataflow = calculatePassthroughDataflow(classResourceByName, classMap, inheritanceMap, sortedMethods, config.getSerializableDecider(methodMap, inheritanceMap));//计算生成passthrough数据流,涉及到字节码分析 } ... ... private List<MethodReference.Handle> topologicallySortMethodCalls() { Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<MethodReference.Handle>> outgoingReferences = new HashMap<>(); for (Map.Entry<MethodReference.Handle, Set<MethodReference.Handle>> entry : methodCalls.entrySet()) { MethodReference.Handle method = entry.getKey(); outgoingReferences.put(method, new HashSet<>(entry.getValue())); } // 对所有方法构成的图执行逆拓扑排序 LOGGER.debug("Performing topological sort..."); Set<MethodReference.Handle> dfsStack = new HashSet<>(); Set<MethodReference.Handle> visitedNodes = new HashSet<>(); List<MethodReference.Handle> sortedMethods = new ArrayList<>(outgoingReferences.size()); for (MethodReference.Handle root : outgoingReferences.keySet()) { dfsTsort(outgoingReferences, sortedMethods, visitedNodes, dfsStack, root); } LOGGER.debug(String.format("Outgoing references %d, sortedMethods %d", outgoingReferences.size(), sortedMethods.size())); return sortedMethods; } ... ... private static void dfsTsort(Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<MethodReference.Handle>> outgoingReferences, List<MethodReference.Handle> sortedMethods, Set<MethodReference.Handle> visitedNodes, Set<MethodReference.Handle> stack, MethodReference.Handle node) { if (stack.contains(node)) {//防止在dfs一条方法调用链中进入循环 return; } if (visitedNodes.contains(node)) {//防止对某个方法及子方法重复排序 return; } Set<MethodReference.Handle> outgoingRefs = outgoingReferences.get(node); if (outgoingRefs == null) { return; } stack.add(node); for (MethodReference.Handle child : outgoingRefs) { dfsTsort(outgoingReferences, sortedMethods, visitedNodes, stack, child); } stack.remove(node); visitedNodes.add(node); sortedMethods.add(node); } } |
拓扑排序
有向无环图(DAG)才有拓扑排序,非 DAG 图没有拓扑排序。 当有向无环图满足以下条件时:
- 每一个顶点出现且只出现一次
- 若A在序列中排在B的前面,则在图中不存在从B到A的路径
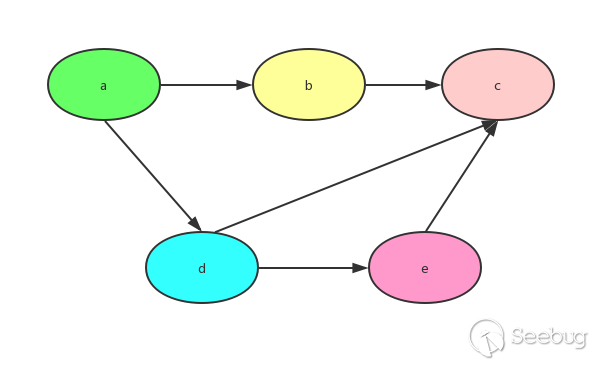
这样的图,是一个拓扑排序的图。树结构其实可以转化为拓扑排序,而拓扑排序 不一定能够转化为树。
以上面的拓扑排序图为例,用一个字典表示图结构
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
graph = { "a": ["b","d"], "b": ["c"], "d": ["e","c"], "e": ["c"], "c": [], } |
代码实现
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
graph = { "a": ["b","d"], "b": ["c"], "d": ["e","c"], "e": ["c"], "c": [], } def TopologicalSort(graph): degrees = dict((u, 0) for u in graph) for u in graph: for v in graph[u]: degrees[v] += 1 #入度为0的插入队列 queue = [u for u in graph if degrees[u] == 0] res = [] while queue: u = queue.pop() res.append(u) for v in graph[u]: # 移除边,即将当前元素相关元素的入度-1 degrees[v] -= 1 if degrees[v] == 0: queue.append(v) return res print(TopologicalSort(graph)) # ['a', 'd', 'e', 'b', 'c'] |
但是在方法的调用中,我们希望最后的结果是c、b、e、d、a,这一步需要逆拓扑排序,正向排序使用的BFS,那么得到相反结果可以使用DFS。为什么在方法调用中需要使用逆拓扑排序呢,这与生成passthrough数据流有关。看下面一个例子:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
... public String parentMethod(String arg){ String vul = Obj.childMethod(arg); return vul; } ... |
那么这里arg与返回值到底有没有关系呢?假设Obj.childMethod为
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
... public String childMethod(String carg){ return carg.toString(); } ... |
由于childMethod的返回值carg与有关,那么可以判定parentMethod的返回值与参数arg是有关系的。所以如果存在子方法调用并传递了父方法参数给子方法时,需要先判断子方法返回值与子方法参数的关系。因此需要让子方法的判断在前面,这就是为什么要进行逆拓扑排序。
从下图可以看出outgoingReferences的数据结构为:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
{ method1:(method2,method3,method4), method5:(method1,method6), ... } |
而这个结构正好适合逆拓扑排序
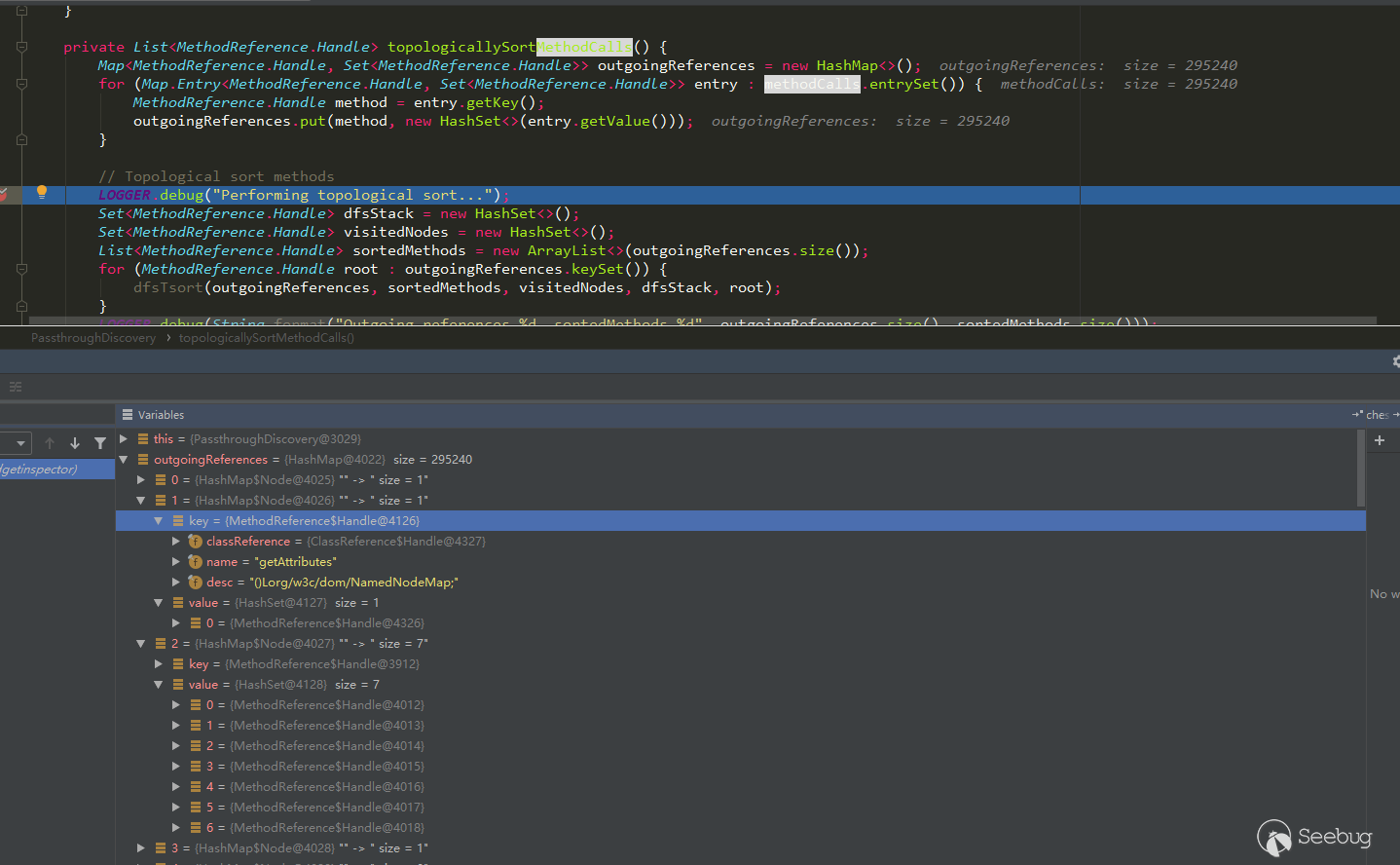
但是上面说拓扑排序时不能形成环,但是在方法调用中肯定是会存在环的。作者是如何避免的呢?
在上面的dfsTsort实现代码中可以看到使用了stack和visitedNodes,stack保证了在进行逆拓扑排序时不会形成环,visitedNodes避免了重复排序。使用如下一个调用图来演示过程:
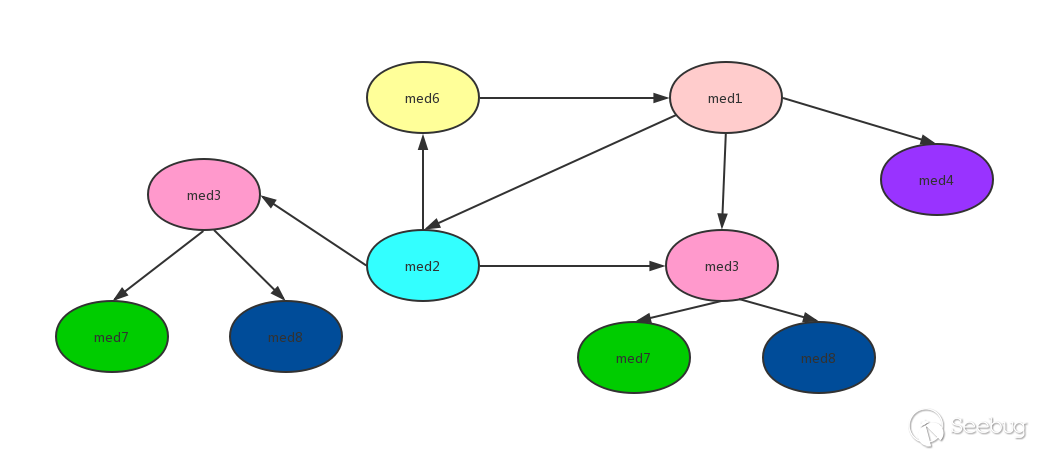
从图中可以看到有环med1->med2->med6->med1,并且有重复的调用med3,严格来说并不能进行逆拓扑排序,但是通过stack、visited记录访问过的方法,就能实现逆拓扑排序。为了方便解释把上面的图用一个树来表示:
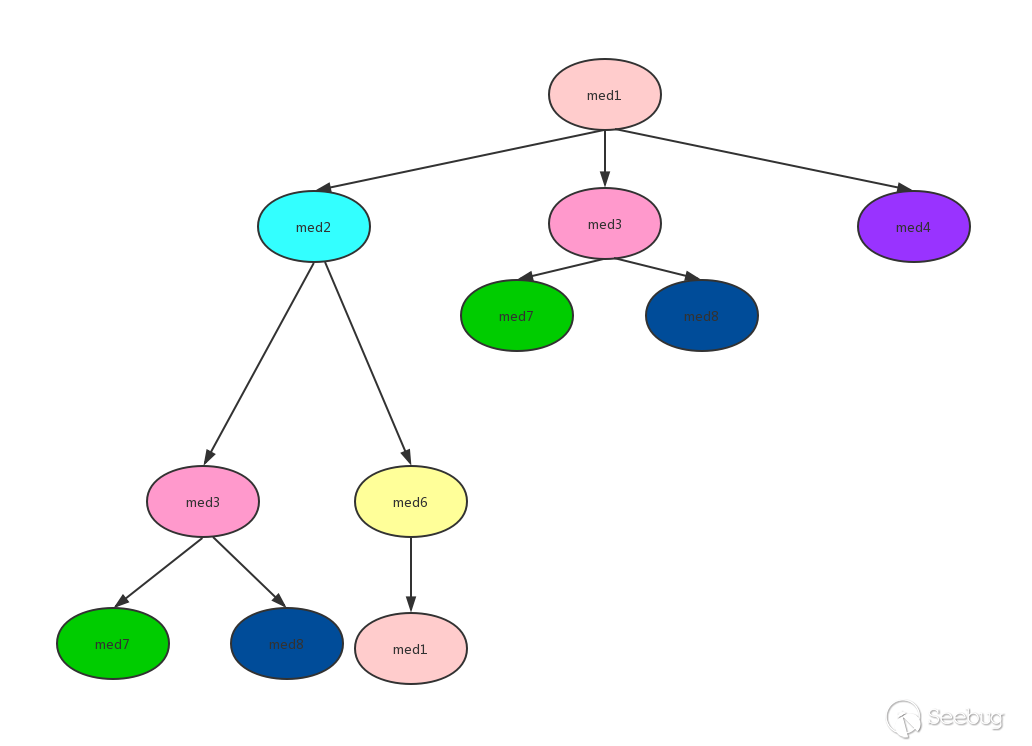
对上图进行逆拓扑排序(DFS方式):
从med1开始,先将med1加入stack中,此时stack、visited、sortedmethods状态如下:
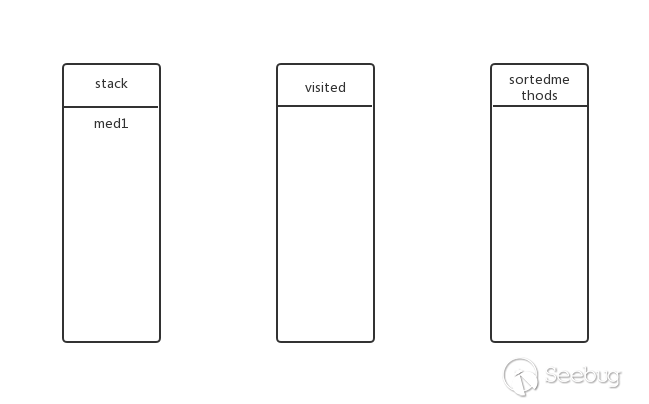
med1还有子方法?有,继续深度遍历。将med2放入stack,此时的状态:
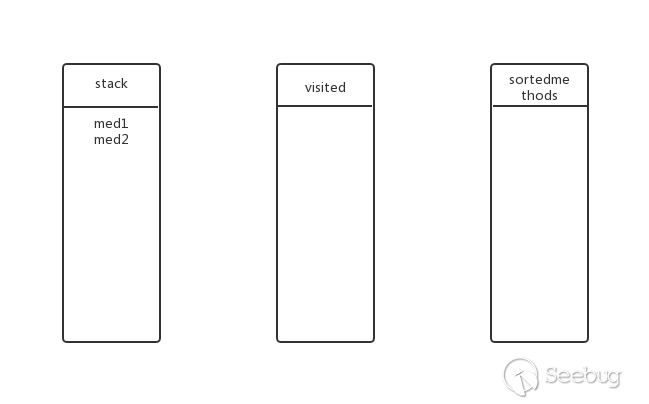
med2有子方法吗?有,继续深度遍历。将med3放入stack,此时的状态:
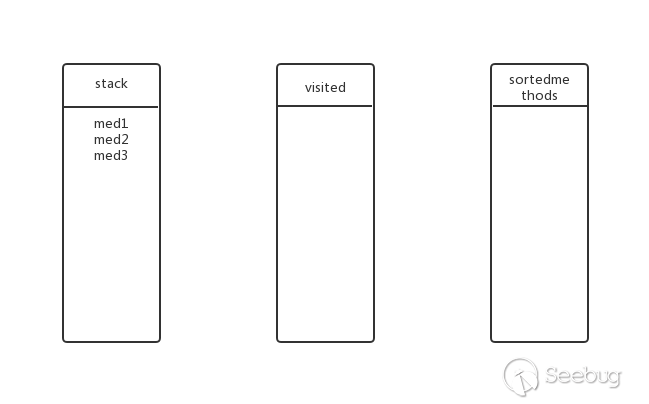
med3有子方法吗?有,继续深度遍历。将med7放入stack,此时的状态:
med7有子方法吗?没有,从stack中弹出med7并加入visited和sortedmethods,此时的状态:

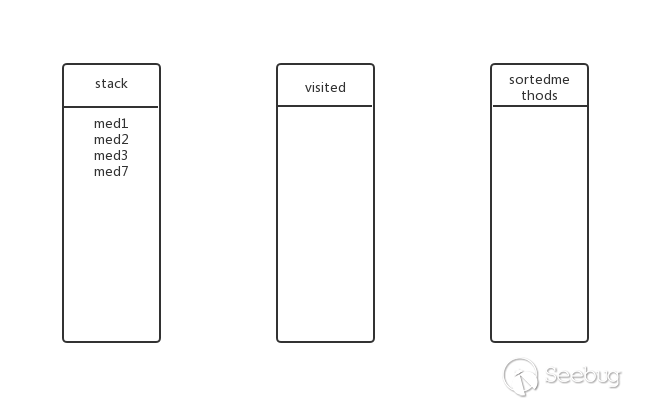
回溯到上一层,med3还有其他子方法吗?有,med8,将med8放入stack,此时的状态:

med8还有子方法吗?没有,弹出stack,加入visited与sortedmethods,此时的状态:
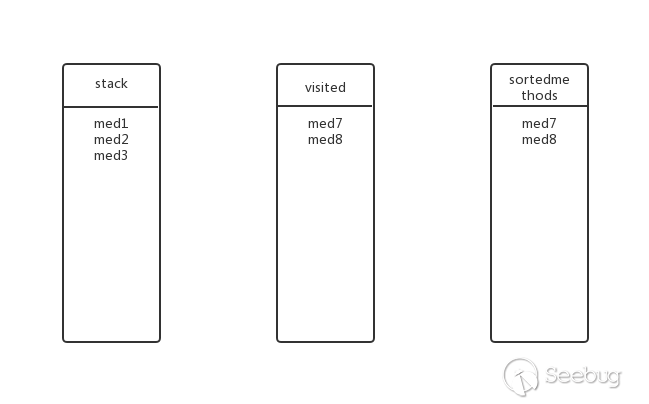
回溯到上一层,med3还有其他子方法吗?没有了,弹出stack,加入visited与sortedmethods,此时的状态:
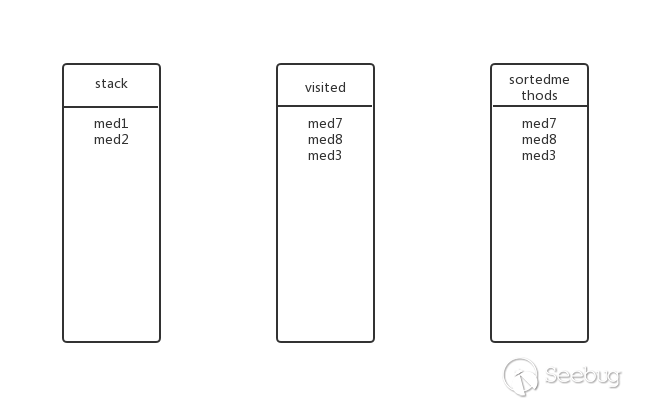
回溯到上一层,med2还有其他子方法吗?有,med6,将med6加入stack,此时的状态:
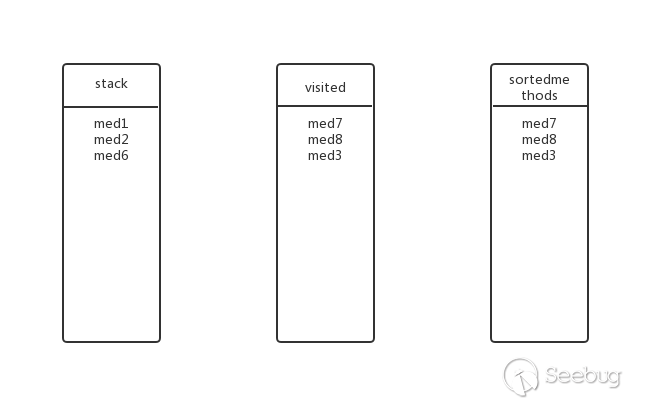
med6还有子方法吗?有,med1,med1在stack中?不加入,抛弃。此时状态和上一步一样
回溯到上一层,med6还有其他子方法吗?没有了,弹出stack,加入visited和sortedmethods,此时的状态:
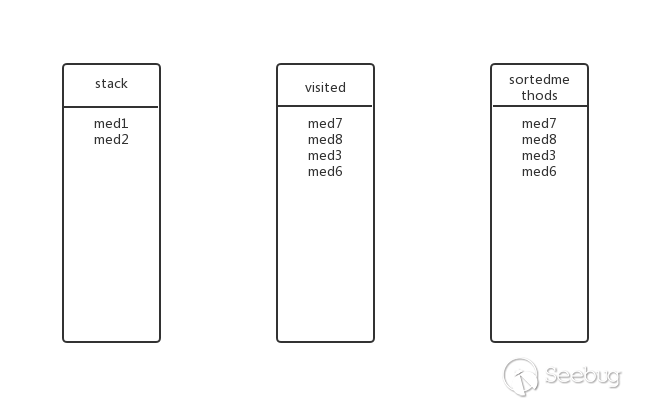
回溯到上一层,med2还有其他子方法吗?没有了,弹出stack,加入visited和sortedmethods,此时的状态:

回溯到上一层,med1还有其他子方法吗?有,med3,med3在visited中?在,抛弃。
回溯到上一层,med1还有其他子方法吗?有,med4,将med4加入stack,此时的状态:

med4还有其他子方法吗?没有,弹出stack,加入visited和sortedmethods中,此时的状态:
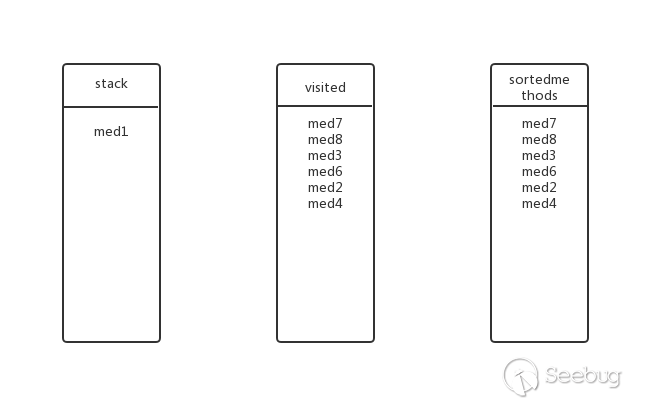
回溯到上一层,med1还有其他子方法吗?没有了,弹出stack,加入visited和sortedmethods中,此时的状态(即最终状态):
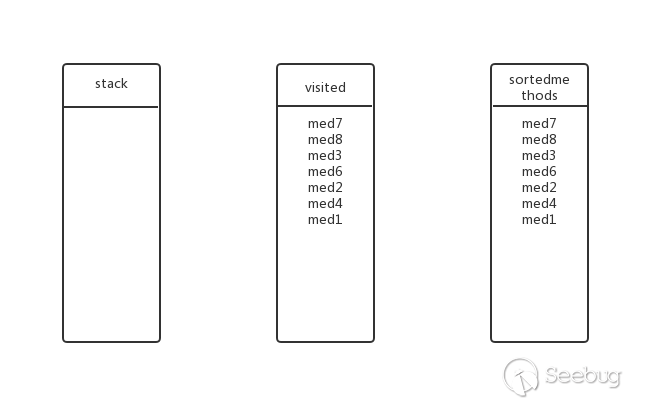
所以最后的逆拓扑排序结果为:med7、med8、med3、med6、med2、med4、med1。
生成passthrough数据流
在calculatePassthroughDataflow中遍历了sortedmethods,并通过字节码分析,生成了方法返回值与参数关系的passthrough数据流。注意到下面的序列化决定器,作者内置了三种:JDK、Jackson、Xstream,会根据具体的序列化决定器判定决策过程中的类是否符合对应库的反序列化要求,不符合的就跳过:
- 对于JDK(ObjectInputStream),类否继承了Serializable接口
- 对于Jackson,类是否存在0参构造器
- 对于Xstream,类名能否作为有效的XML标签
生成passthrough数据流代码:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
... private static Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<Integer>> calculatePassthroughDataflow(Map<String, ClassResourceEnumerator.ClassResource> classResourceByName, Map<ClassReference.Handle, ClassReference> classMap, InheritanceMap inheritanceMap, List<MethodReference.Handle> sortedMethods, SerializableDecider serializableDecider) throws IOException { final Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<Integer>> passthroughDataflow = new HashMap<>(); for (MethodReference.Handle method : sortedMethods) {//依次遍历sortedmethods,并且每个方法的子方法判定总在这个方法之前,这是通过的上面的逆拓扑排序实现的。 if (method.getName().equals("<clinit>")) { continue; } ClassResourceEnumerator.ClassResource classResource = classResourceByName.get(method.getClassReference().getName()); try (InputStream inputStream = classResource.getInputStream()) { ClassReader cr = new ClassReader(inputStream); try { PassthroughDataflowClassVisitor cv = new PassthroughDataflowClassVisitor(classMap, inheritanceMap, passthroughDataflow, serializableDecider, Opcodes.ASM6, method); cr.accept(cv, ClassReader.EXPAND_FRAMES);//通过结合classMap、inheritanceMap、已判定出的passthroughDataflow结果、序列化决定器信息来判定当前method的返回值与参数的关系 passthroughDataflow.put(method, cv.getReturnTaint());//将判定后的method与有关系的污染点加入passthroughDataflow } catch (Exception e) { LOGGER.error("Exception analyzing " + method.getClassReference().getName(), e); } } catch (IOException e) { LOGGER.error("Unable to analyze " + method.getClassReference().getName(), e); } } return passthroughDataflow; } ... |
最后生成了passthrough.dat:
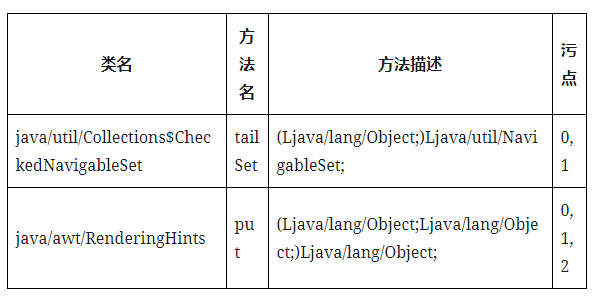
Step3 枚举passthrough调用图
这一步和上一步类似,gadgetinspector 会再次扫描全部的Java方法,但检查的不再是参数与返回结果的关系,而是方法的参数与其所调用的子方法的关系,即子方法的参数是否可以被父方法的参数所影响。那么为什么要进行上一步的生成passthrough数据流呢?由于这一步的判断也是在字节码分析中,所以这里只能先进行一些猜测,如下面这个例子:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
... private MyObject obj; public void parentMethod(Object arg){ ... TestObject obj1 = new TestObject(); Object obj2 = obj1.childMethod1(arg); this.obj.childMethod(obj2); ... } ... |
如果不进行生成passthrough数据流操作,就无法判断TestObject.childMethod1的返回值是否会受到参数1的影响,也就无法继续判断parentMethod的arg参数与子方法MyObject.childmethod的参数传递关系。
作者给出的例子:
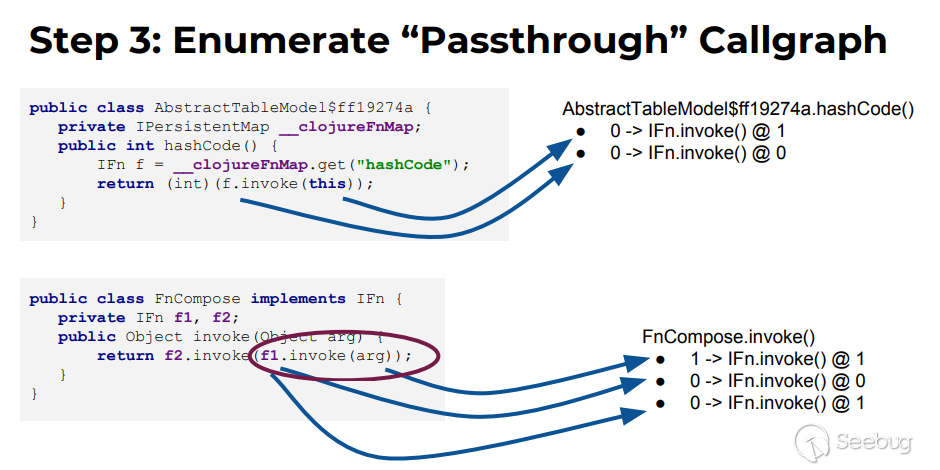
AbstractTableModel$ff19274a.hashcode与子方法IFn.invoke:
- AbstractTableModel$ff19274a.hashcode的this(0参)传递给了IFn.invoke的1参,表示为0->IFn.invoke()@1
- 由于f是通过this.__clojureFnMap(0参)获取的,而f又为IFn.invoke()的this(0参),即AbstractTableModel$ff19274a.hashcode的0参传递给了IFn.invoke的0参,表示为0->IFn.invoke()@0
FnCompose.invoke与子方法IFn.invoke:
- FnCompose.invoked的arg(1参)传递给了IFn.invoke的1参,表示为1->IFn.invoke()@1
- f1为FnCompose的属性(this,0参),被做为了IFn.invoke的this(0参数)传递,表示为0->IFn.invoke()@1
- f1.invoke(arg)做为一个整体被当作1参传递给了IFn.invoke,由于f1在序列化时我们可以控制具体是IFn的哪个实现类,所以具体调用哪个实现类的invoke也相当于能够控制,即f1.invoke(arg)这个整体可以视为0参数传递给了IFn.invoke的1参(这里只是进行的简单猜测,具体实现在字节码分析中,可能也体现了作者说的合理的风险判断吧),表示为0->IFn.invoke()@1
在这一步中,gadgetinspector也是利用ASM来进行字节码的分析,主要逻辑是在类CallGraphDiscovery和ModelGeneratorClassVisitor中。在ModelGeneratorClassVisitor中通过标记追踪JVM虚拟机在执行方法时的stack和localvar,最终得到方法的参数与其所调用的子方法的参数传递关系。
生成passthrough调用图代码(暂时省略ModelGeneratorClassVisitor的实现,涉及到字节码分析):
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
public class CallGraphDiscovery { private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CallGraphDiscovery.class); private final Set<GraphCall> discoveredCalls = new HashSet<>(); public void discover(final ClassResourceEnumerator classResourceEnumerator, GIConfig config) throws IOException { Map<MethodReference.Handle, MethodReference> methodMap = DataLoader.loadMethods();//加载所有方法 Map<ClassReference.Handle, ClassReference> classMap = DataLoader.loadClasses();//加载所有类 InheritanceMap inheritanceMap = InheritanceMap.load();//加载继承图 Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<Integer>> passthroughDataflow = PassthroughDiscovery.load();//加载passthrough数据流 SerializableDecider serializableDecider = config.getSerializableDecider(methodMap, inheritanceMap);//序列化决定器 for (ClassResourceEnumerator.ClassResource classResource : classResourceEnumerator.getAllClasses()) { try (InputStream in = classResource.getInputStream()) { ClassReader cr = new ClassReader(in); try { cr.accept(new ModelGeneratorClassVisitor(classMap, inheritanceMap, passthroughDataflow, serializableDecider, Opcodes.ASM6), ClassReader.EXPAND_FRAMES);//通过结合classMap、inheritanceMap、passthroughDataflow结果、序列化决定器信息来判定当前method参数与子方法传递调用关系 } catch (Exception e) { LOGGER.error("Error analyzing: " + classResource.getName(), e); } } } } |
最后生成了passthrough.dat:
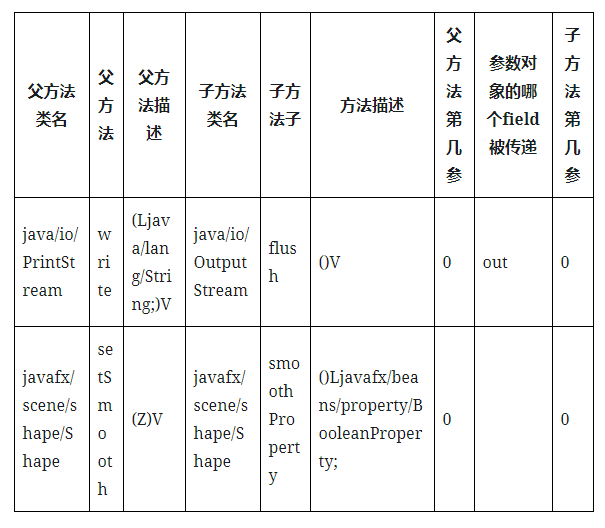
Step4 搜索可用的source
这一步会根据已知的反序列化漏洞的入口,检查所有可以被触发的方法。例如,在利用链中使用代理时,任何可序列化并且是java/lang/reflect/InvocationHandler子类的invoke方法都可以视为source。这里还会根据具体的反序列化库决定类是否能被序列化。
搜索可用的source:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 |
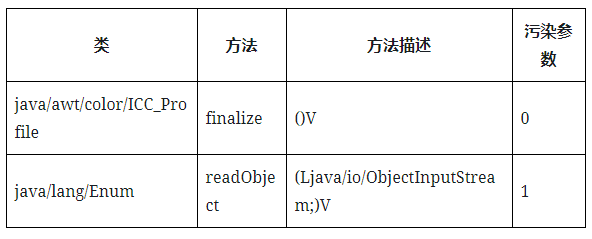
public class SimpleSourceDiscovery extends SourceDiscovery { @Override public void discover(Map<ClassReference.Handle, ClassReference> classMap, Map<MethodReference.Handle, MethodReference> methodMap, InheritanceMap inheritanceMap) { final SerializableDecider serializableDecider = new SimpleSerializableDecider(inheritanceMap); for (MethodReference.Handle method : methodMap.keySet()) { if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(serializableDecider.apply(method.getClassReference()))) { if (method.getName().equals("finalize") && method.getDesc().equals("()V")) { addDiscoveredSource(new Source(method, 0)); } } } // 如果类实现了readObject,则传入的ObjectInputStream被认为是污染的 for (MethodReference.Handle method : methodMap.keySet()) { if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(serializableDecider.apply(method.getClassReference()))) { if (method.getName().equals("readObject") && method.getDesc().equals("(Ljava/io/ObjectInputStream;)V")) { addDiscoveredSource(new Source(method, 1)); } } } // 使用代理技巧时,任何扩展了serializable and InvocationHandler的类会受到污染。 for (ClassReference.Handle clazz : classMap.keySet()) { if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(serializableDecider.apply(clazz)) && inheritanceMap.isSubclassOf(clazz, new ClassReference.Handle("java/lang/reflect/InvocationHandler"))) { MethodReference.Handle method = new MethodReference.Handle( clazz, "invoke", "(Ljava/lang/Object;Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;[Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;"); addDiscoveredSource(new Source(method, 0)); } } // hashCode()或equals()是将对象放入HashMap的标准技巧的可访问入口点 for (MethodReference.Handle method : methodMap.keySet()) { if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(serializableDecider.apply(method.getClassReference()))) { if (method.getName().equals("hashCode") && method.getDesc().equals("()I")) { addDiscoveredSource(new Source(method, 0)); } if (method.getName().equals("equals") && method.getDesc().equals("(Ljava/lang/Object;)Z")) { addDiscoveredSource(new Source(method, 0)); addDiscoveredSource(new Source(method, 1)); } } } // 使用比较器代理,可以跳转到任何groovy Closure的call()/doCall()方法,所有的args都被污染 // https://github.com/frohoff/ysoserial/blob/master/src/main/java/ysoserial/payloads/Groovy1.java for (MethodReference.Handle method : methodMap.keySet()) { if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(serializableDecider.apply(method.getClassReference())) && inheritanceMap.isSubclassOf(method.getClassReference(), new ClassReference.Handle("groovy/lang/Closure")) && (method.getName().equals("call") || method.getName().equals("doCall"))) { addDiscoveredSource(new Source(method, 0)); Type[] methodArgs = Type.getArgumentTypes(method.getDesc()); for (int i = 0; i < methodArgs.length; i++) { addDiscoveredSource(new Source(method, i + 1)); } } } } ... |
这一步的结果会保存在文件sources.dat中:
Step5 搜索生成调用链
这一步会遍历全部的source,并在callgraph.dat中递归查找所有可以继续传递污点参数的子方法调用,直至遇到sink中的方法。
搜索生成调用链:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 |
public class GadgetChainDiscovery { private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(GadgetChainDiscovery.class); private final GIConfig config; public GadgetChainDiscovery(GIConfig config) { this.config = config; } public void discover() throws Exception { Map<MethodReference.Handle, MethodReference> methodMap = DataLoader.loadMethods(); InheritanceMap inheritanceMap = InheritanceMap.load(); Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<MethodReference.Handle>> methodImplMap = InheritanceDeriver.getAllMethodImplementations( inheritanceMap, methodMap);//得到方法的所有子类方法实现(被子类重写的方法) final ImplementationFinder implementationFinder = config.getImplementationFinder( methodMap, methodImplMap, inheritanceMap); //将方法的所有子类方法实现保存到methodimpl.dat try (Writer writer = Files.newBufferedWriter(Paths.get("methodimpl.dat"))) { for (Map.Entry<MethodReference.Handle, Set<MethodReference.Handle>> entry : methodImplMap.entrySet()) { writer.write(entry.getKey().getClassReference().getName()); writer.write("\t"); writer.write(entry.getKey().getName()); writer.write("\t"); writer.write(entry.getKey().getDesc()); writer.write("\n"); for (MethodReference.Handle method : entry.getValue()) { writer.write("\t"); writer.write(method.getClassReference().getName()); writer.write("\t"); writer.write(method.getName()); writer.write("\t"); writer.write(method.getDesc()); writer.write("\n"); } } } //方法调用map,key为父方法,value为子方法与父方法参数传递关系 Map<MethodReference.Handle, Set<GraphCall>> graphCallMap = new HashMap<>(); for (GraphCall graphCall : DataLoader.loadData(Paths.get("callgraph.dat"), new GraphCall.Factory())) { MethodReference.Handle caller = graphCall.getCallerMethod(); if (!graphCallMap.containsKey(caller)) { Set<GraphCall> graphCalls = new HashSet<>(); graphCalls.add(graphCall); graphCallMap.put(caller, graphCalls); } else { graphCallMap.get(caller).add(graphCall); } } //exploredMethods保存在调用链从查找过程中已经访问过的方法节点,methodsToExplore保存调用链 Set<GadgetChainLink> exploredMethods = new HashSet<>(); LinkedList<GadgetChain> methodsToExplore = new LinkedList<>(); //加载所有sources,并将每个source作为每条链的第一个节点 for (Source source : DataLoader.loadData(Paths.get("sources.dat"), new Source.Factory())) { GadgetChainLink srcLink = new GadgetChainLink(source.getSourceMethod(), source.getTaintedArgIndex()); if (exploredMethods.contains(srcLink)) { continue; } methodsToExplore.add(new GadgetChain(Arrays.asList(srcLink))); exploredMethods.add(srcLink); } long iteration = 0; Set<GadgetChain> discoveredGadgets = new HashSet<>(); //使用广度优先搜索所有从source到sink的调用链 while (methodsToExplore.size() > 0) { if ((iteration % 1000) == 0) { LOGGER.info("Iteration " + iteration + ", Search space: " + methodsToExplore.size()); } iteration += 1; GadgetChain chain = methodsToExplore.pop();//从队首弹出一条链 GadgetChainLink lastLink = chain.links.get(chain.links.size()-1);//取这条链最后一个节点 Set<GraphCall> methodCalls = graphCallMap.get(lastLink.method);//获取当前节点方法所有子方法与当前节点方法参数传递关系 if (methodCalls != null) { for (GraphCall graphCall : methodCalls) { if (graphCall.getCallerArgIndex() != lastLink.taintedArgIndex) { //如果当前节点方法的污染参数与当前子方法受父方法参数影响的Index不一致则跳过 continue; } Set<MethodReference.Handle> allImpls = implementationFinder.getImplementations(graphCall.getTargetMethod());//获取子方法所在类的所有子类重写方法 for (MethodReference.Handle methodImpl : allImpls) { GadgetChainLink newLink = new GadgetChainLink(methodImpl, graphCall.getTargetArgIndex());//新方法节点 if (exploredMethods.contains(newLink)) { //如果新方法已近被访问过了,则跳过,这里能减少开销。但是这一步跳过会使其他链/分支链经过此节点时,由于已经此节点被访问过了,链会在这里断掉。那么如果这个条件去掉就能实现找到所有链了吗?这里去掉会遇到环状问题,造成路径无限增加... continue; } GadgetChain newChain = new GadgetChain(chain, newLink);//新节点与之前的链组成新链 if (isSink(methodImpl, graphCall.getTargetArgIndex(), inheritanceMap)) {//如果到达了sink,则加入discoveredGadgets discoveredGadgets.add(newChain); } else { //新链加入队列 methodsToExplore.add(newChain); //新节点加入已访问集合 exploredMethods.add(newLink); } } } } } //保存搜索到的利用链到gadget-chains.txt try (OutputStream outputStream = Files.newOutputStream(Paths.get("gadget-chains.txt")); Writer writer = new OutputStreamWriter(outputStream, StandardCharsets.UTF_8)) { for (GadgetChain chain : discoveredGadgets) { printGadgetChain(writer, chain); } } LOGGER.info("Found {} gadget chains.", discoveredGadgets.size()); } ... |
作者给出的sink方法:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 |
private boolean isSink(MethodReference.Handle method, int argIndex, InheritanceMap inheritanceMap) { if (method.getClassReference().getName().equals("java/io/FileInputStream") && method.getName().equals("<init>")) { return true; } if (method.getClassReference().getName().equals("java/io/FileOutputStream") && method.getName().equals("<init>")) { return true; } if (method.getClassReference().getName().equals("java/nio/file/Files") && (method.getName().equals("newInputStream") || method.getName().equals("newOutputStream") || method.getName().equals("newBufferedReader") || method.getName().equals("newBufferedWriter"))) { return true; } if (method.getClassReference().getName().equals("java/lang/Runtime") && method.getName().equals("exec")) { return true; } /* if (method.getClassReference().getName().equals("java/lang/Class") && method.getName().equals("forName")) { return true; } if (method.getClassReference().getName().equals("java/lang/Class") && method.getName().equals("getMethod")) { return true; } */ // If we can invoke an arbitrary method, that's probably interesting (though this doesn't assert that we // can control its arguments). Conversely, if we can control the arguments to an invocation but not what // method is being invoked, we don't mark that as interesting. if (method.getClassReference().getName().equals("java/lang/reflect/Method") && method.getName().equals("invoke") && argIndex == 0) { return true; } if (method.getClassReference().getName().equals("java/net/URLClassLoader") && method.getName().equals("newInstance")) { return true; } if (method.getClassReference().getName().equals("java/lang/System") && method.getName().equals("exit")) { return true; } if (method.getClassReference().getName().equals("java/lang/Shutdown") && method.getName().equals("exit")) { return true; } if (method.getClassReference().getName().equals("java/lang/Runtime") && method.getName().equals("exit")) { return true; } if (method.getClassReference().getName().equals("java/nio/file/Files") && method.getName().equals("newOutputStream")) { return true; } if (method.getClassReference().getName().equals("java/lang/ProcessBuilder") && method.getName().equals("<init>") && argIndex > 0) { return true; } if (inheritanceMap.isSubclassOf(method.getClassReference(), new ClassReference.Handle("java/lang/ClassLoader")) && method.getName().equals("<init>")) { return true; } if (method.getClassReference().getName().equals("java/net/URL") && method.getName().equals("openStream")) { return true; } // Some groovy-specific sinks if (method.getClassReference().getName().equals("org/codehaus/groovy/runtime/InvokerHelper") && method.getName().equals("invokeMethod") && argIndex == 1) { return true; } if (inheritanceMap.isSubclassOf(method.getClassReference(), new ClassReference.Handle("groovy/lang/MetaClass")) && Arrays.asList("invokeMethod", "invokeConstructor", "invokeStaticMethod").contains(method.getName())) { return true; } return false; } |
对于每个入口节点来说,其全部子方法调用、孙子方法调用等等递归下去,就构成了一棵树。之前的步骤所做的,就相当于生成了这颗树,而这一步所做的,就是从根节点出发,找到一条通往叶子节点的道路,使得这个叶子节点正好是我们所期望的sink方法。gadgetinspector对树的遍历采用的是广度优先(BFS),而且对于已经检查过的节点会直接跳过,这样减少了运行开销,避免了环路,但是丢掉了很多其他链。
这个过程看起来就像下面这样:
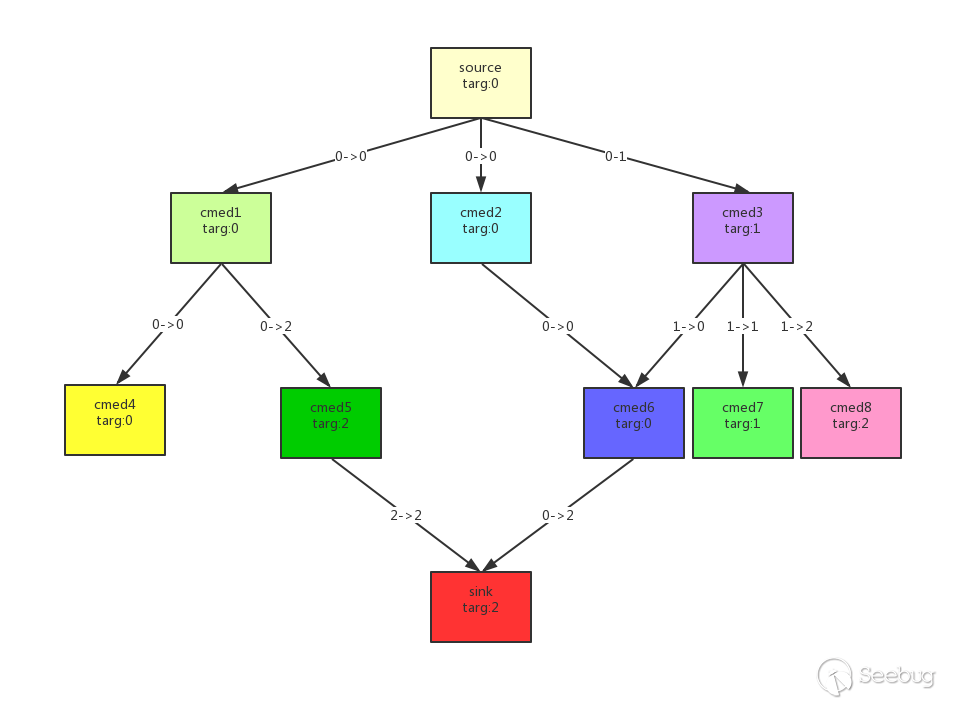
通过污点的传递,最终找到从source->sink的利用链
注:targ表示污染参数的index,0->1这样的表示父方法的0参传递给了子方法的1参
样例分析
现在根据作者的样例写个具体的demo实例来测试下上面这些步骤。
demo如下:
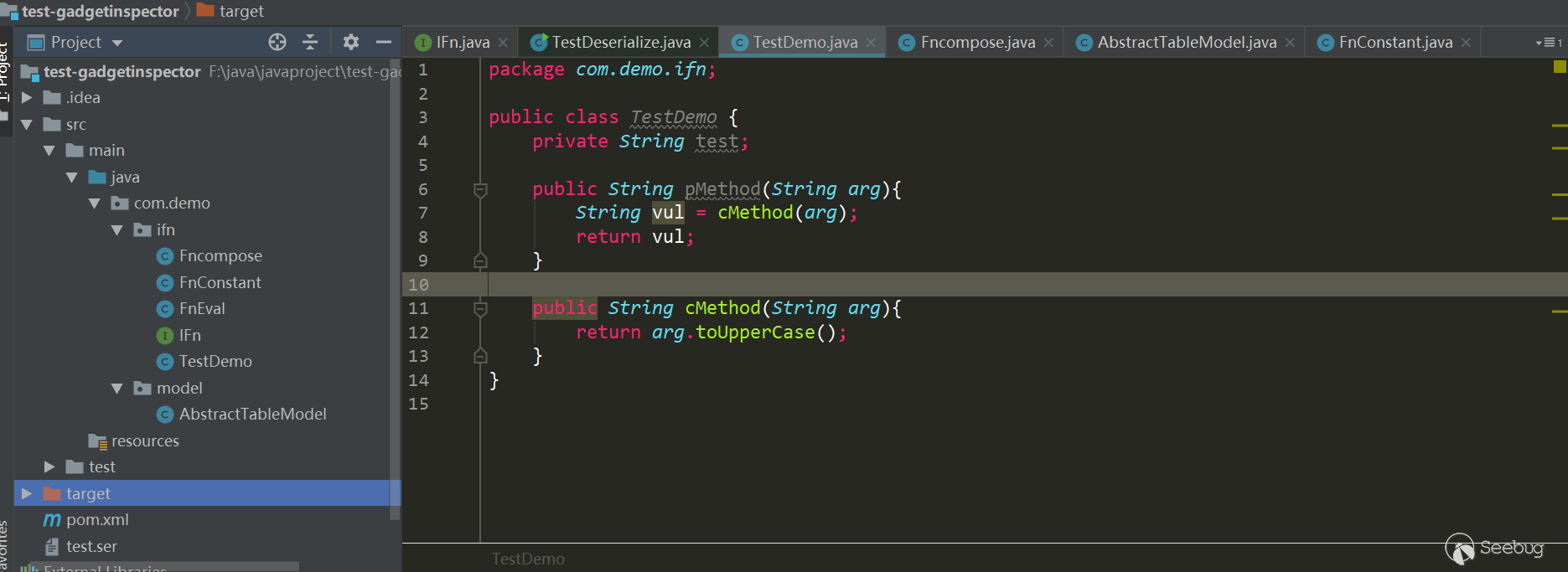
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 |
IFn.java: package com.demo.ifn; import java.io.IOException; public interface IFn { public Object invokeCall(Object arg) throws IOException; } FnEval.java package com.demo.ifn; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.Serializable; public class FnEval implements IFn, Serializable { public FnEval() { } public Object invokeCall(Object arg) throws IOException { return Runtime.getRuntime().exec((String) arg); } } FnConstant.java: package com.demo.ifn; import java.io.Serializable; public class FnConstant implements IFn , Serializable { private Object value; public FnConstant(Object value) { this.value = value; } public Object invokeCall(Object arg) { return value; } } FnCompose.java: package com.demo.ifn; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.Serializable; public class FnCompose implements IFn, Serializable { private IFn f1, f2; public FnCompose(IFn f1, IFn f2) { this.f1 = f1; this.f2 = f2; } public Object invokeCall(Object arg) throws IOException { return f2.invokeCall(f1.invokeCall(arg)); } } TestDemo.java: package com.demo.ifn; public class TestDemo { //测试拓扑排序的正确性 private String test; public String pMethod(String arg){ String vul = cMethod(arg); return vul; } public String cMethod(String arg){ return arg.toUpperCase(); } } AbstractTableModel.java: package com.demo.model; import com.demo.ifn.IFn; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.HashMap; public class AbstractTableModel implements Serializable { private HashMap<String, IFn> __clojureFnMap; public AbstractTableModel(HashMap<String, IFn> clojureFnMap) { this.__clojureFnMap = clojureFnMap; } public int hashCode() { IFn f = __clojureFnMap.get("hashCode"); try { f.invokeCall(this); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return this.__clojureFnMap.hashCode() + 1; } } |
注:下面截图中数据的顺序做了调换,同时数据也只给出com/demo中的数据
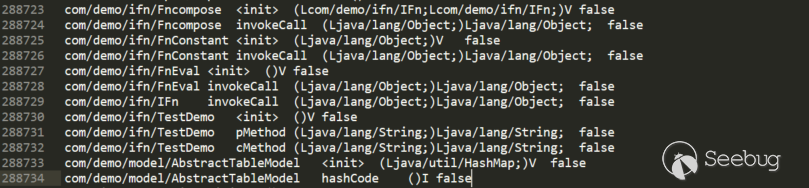
Step1 枚举全部类及每个类所有方法
classes.dat:

methods.dat:
Step2 生成passthrough数据流
passthrough.dat:

可以看到IFn的子类中只有FnConstant的invokeCall在passthrough数据流中,因为其他几个在静态分析中无法判断返回值与参数的关系。同时TestDemo的cMethod与pMethod都在passthrough数据流中,这也说明了拓扑排序那一步的必要性和正确性。
Step3 枚举passthrough调用图
callgraph.dat:
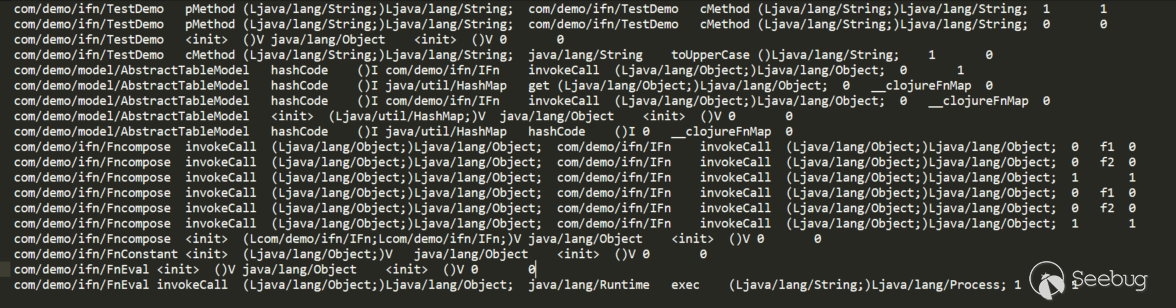
Step4 搜索可用的source
sources.dat:

Step5 搜索生成调用链
在gadget-chains.txt中找到了如下链:
|
1 2 3 |
com/demo/model/AbstractTableModel.hashCode()I (0) com/demo/ifn/FnEval.invokeCall(Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object; (1) java/lang/Runtime.exec(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/Process; (1) |
可以看到选择的确实是找了一条最短的路径,并没有经过FnCompose、FnConstant路径。
环路造成路径爆炸
上面流程分析第五步中说到,如果去掉已访问过节点的判断会怎么样呢,能不能生成经过FnCompose、FnConstant的调用链呢?
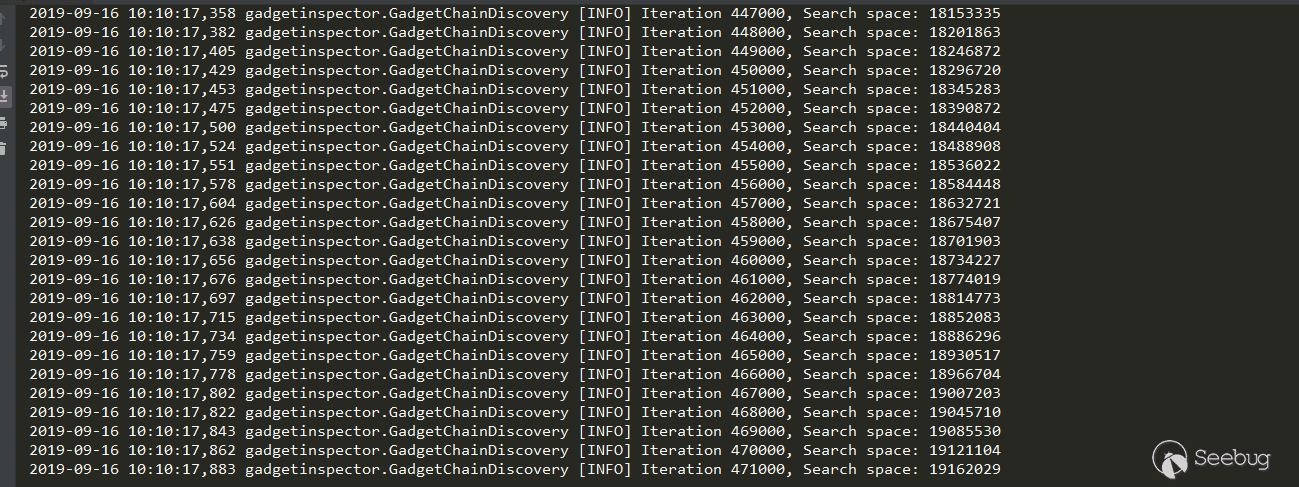
陷入了爆炸状态,Search space无限增加,其中必定存在环路。作者使用的策略是访问过的节点就不再访问了,这样解决的环路问题,但是丢失了其他链。
比如上面的FnCompose类:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
public class Fncompose implements IFn{ private IFn f1,f2; public Object invoke(Object arg){ return f2.invoke(f1.invoke(arg)); } } |
由于IFn是接口,所以在调用链生成中会查找是它的子类,假如f1,f2都是FnCompose类的对象,这样形成了环路。
隐式调用
测试隐式调用看工具能否发现,将FnEval.java做一些修改:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
FnEval.java package com.demo.ifn; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.Serializable; public class FnEval implements IFn, Serializable { private String cmd; public FnEval() { } @Override public String toString() { try { Runtime.getRuntime().exec(this.cmd); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return "FnEval{}"; } public Object invokeCall(Object arg) throws IOException { this.cmd = (String) arg; return this + " test"; } } |
结果:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
com/demo/model/AbstractTableModel.hashCode()I (0) com/demo/ifn/FnEval.invokeCall(Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object; (0) java/lang/StringBuilder.append(Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/StringBuilder; (1) java/lang/String.valueOf(Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/String; (0) com/demo/ifn/FnEval.toString()Ljava/lang/String; (0) java/lang/Runtime.exec(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/Process; (1) |
隐式调用了tostring方法,说明在字节码分析中做了查找隐式调用这一步。
不遵循反射调用
在github的工具说明中,作者也说到了在静态分析中这个工具的盲点,像下面这中FnEval.class.getMethod("exec", String.class).invoke(null, arg)写法是不遵循反射调用的,将FnEval.java修改:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
FnEval.java package com.demo.ifn; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.Serializable; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; public class FnEval implements IFn, Serializable { public FnEval() { } public static void exec(String arg) throws IOException { Runtime.getRuntime().exec(arg); } public Object invokeCall(Object arg) throws IOException { try { return FnEval.class.getMethod("exec", String.class).invoke(null, arg); } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } } |
经过测试,确实没有发现。但是将FnEval.class.getMethod("exec", String.class).invoke(null, arg)改为this.getClass().getMethod("exec", String.class).invoke(null, arg)这种写法却是可以发现的。
特殊语法
测试一下比较特殊的语法呢,比如lambda语法?将FnEval.java做一些修改:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
FnEval.java: package com.demo.ifn; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.Serializable; public class FnEval implements IFn, Serializable { public FnEval() { } interface ExecCmd { public Object exec(String cmd) throws IOException; } public Object invokeCall(Object arg) throws IOException { ExecCmd execCmd = cmd -> { return Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd); }; return execCmd.exec((String) arg); } } |
经过测试,没有检测到这条利用链。说明目前语法分析那一块还没有对特殊语法分析。
匿名内部类
测试匿名内部类,将FnEval.java做一些修改:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
FnEval.java: package com.demo.ifn; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.Serializable; public class FnEval implements IFn, Serializable { public FnEval() { } interface ExecCmd { public Object exec(String cmd) throws IOException; } public Object callExec(ExecCmd execCmd, String cmd) throws IOException { return execCmd.exec(cmd); } public Object invokeCall(Object arg) throws IOException { return callExec(new ExecCmd() { @Override public Object exec(String cmd) throws IOException { return Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd); } }, (String) arg); } } |
经过测试,没有检测到这条利用链。说明目前语法分析那一块还没有对匿名内部类的分析。
sink->source?
既然能source->sink,那么能不能sink->source呢?因为搜索source->sink时,source和sink都是已知的,如果搜索sink->source时,sink与soure也是已知的,那么source->sink与sink->source好像没有什么区别?如果能将source总结为参数可控的一类特征,那么sink->source这种方式是一种非常好的方式,不仅能用在反序列化漏洞中,还能用在其他漏洞中(例如模板注入)。但是这里也还有一些问题,比如反序列化是将this以及类的属性都当作了0参,因为反序列化时这些都是可控的,但是在其他漏洞中这些就不一定可控了。
目前还不知道具体如何实现以及会有哪些问题,暂时先不写。
缺陷
目前还没有做过大量测试,只是从宏观层面分析了这个工具的大致原理。结合平安集团分析文章以及上面的测试目前可以总结出一下几个缺点(不止这些缺陷):
- callgraph生成不完整
- 调用链搜索结果不完整,这是由于查找策略导致的
- 一些特殊语法、匿名内部类还不支持
- ...
设想与改进
- 对以上几个缺陷进行改进
- 结合已知的利用链(如ysoserial等)不断测试
- 尽可能列出所有链并结合人工筛选判断,而作者使用的策略是只要经过这个节点有一条链,其他链经过这个节点时就不再继续寻找下去。主要解决的就是最后那个调用链环路问题,目前看到几种方式:
- DFS+最大深度限制
- 继续使用BFS,人工检查生成的调用链,把无效的callgraph去掉,重复运行
- 调用链缓存(这一个暂时还没明白具体怎么解决环路的,只是看到了这个方法)
我的想法是在每条链中维持一个黑名单,每次都检查是否出现了环路,如果在这条链中出现了环路,将造成环路的节点加入黑名单,继续使其走下去。当然虽然没有了环,也能会出现路径无限增长的情况,所以还是需要加入路径长度限制。
- 尝试sink->source的实现
- 多线程同时搜索多条利用链加快速度
- ...
最后
在原理分析的时候,忽略了字节码分析的细节,有的地方只是暂时猜测与测试得出的结果,所以可能存在一些错误。字节码分析那一块是很重要的一环,它对污点的判断、污点的传递调用等起着很重要的作用,如果这些部分出现了问题,整个搜索过程就会出现问题。由于ASM框架对使用人员要求较高,所以需要要掌握JVM相关的知识才能较好使用ASM框架,所以接下来的就是开始学习JVM相关的东西。这篇文章只是从宏观层面分析这个工具的原理,也算是给自己增加些信心,至少明白这个工具不是无法理解和无法改进的,同时后面再接触这个工具进行改进时也会间隔一段时间,回顾起来也方便,其他人如果对这个工具感兴趣也可以参考。等以后熟悉并能操纵Java字节码了,在回头来更新这篇文章并改正可能有错误的地方。
如果这些设想与改进真的实现并且进行了验证,那么这个工具真的是一个得力帮手。但是这些东西要实现还有较长的一段路要走,还没开始实现就预想到了那么多问题,在实现的时候会遇到更多问题。不过好在有一个大致的方向了,接下来就是对各个环节逐一解决了。
参考
- https://i.blackhat.com/us-18/Thu-August-9/us-18-Haken-Automated-Discovery-of-Deserialization-Gadget-Chains.pdf
- https://i.blackhat.com/us-18/Thu-August-9/us-18-Haken-Automated-Discovery-of-Deserialization-Gadget-Chains-wp.pdf
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wPbW6zQ52w8
- https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/RD90-78I7wRogdYdsB-UOg

本文由 Seebug Paper 发布,如需转载请注明来源。本文地址:https://paper.seebug.org/1034/