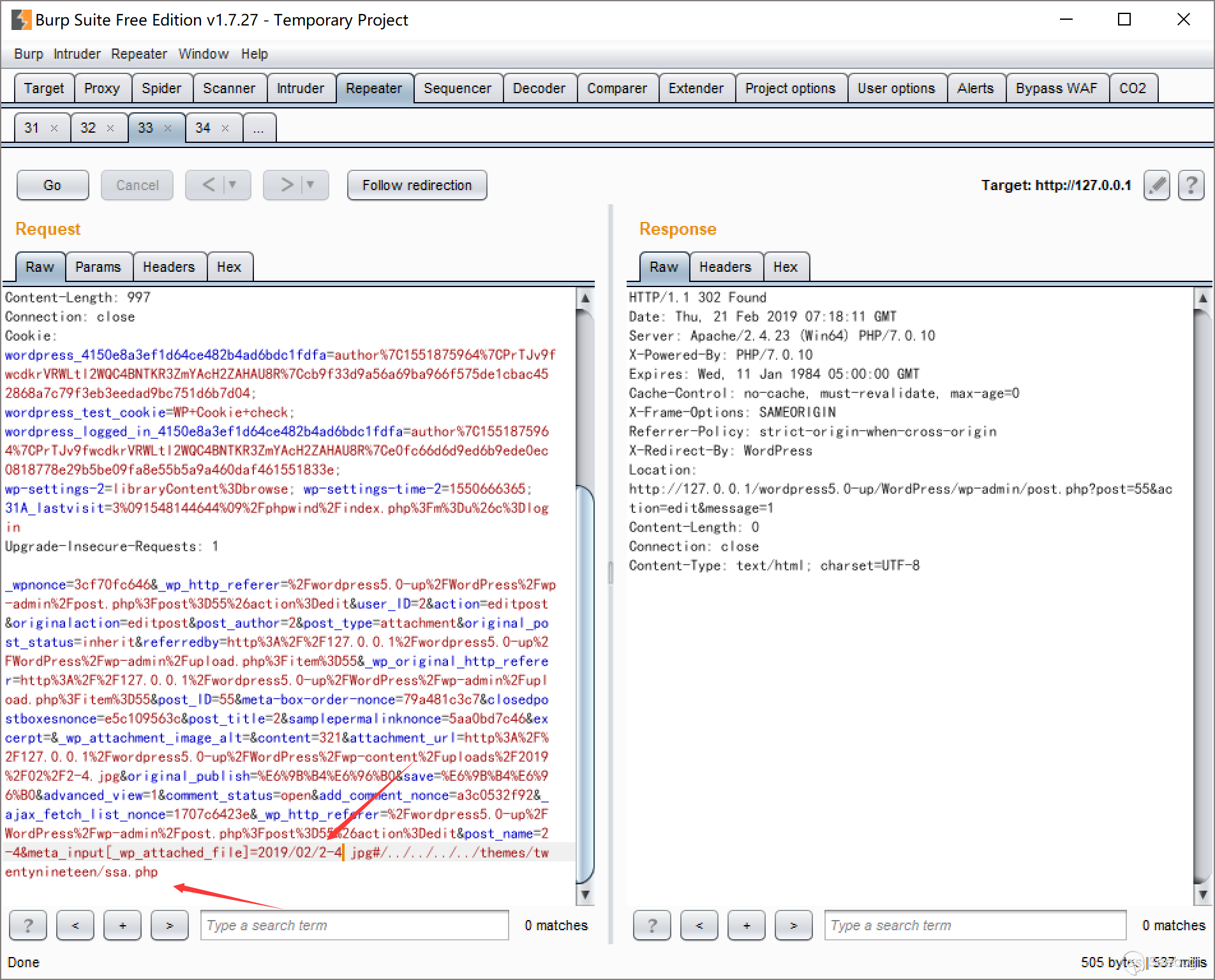
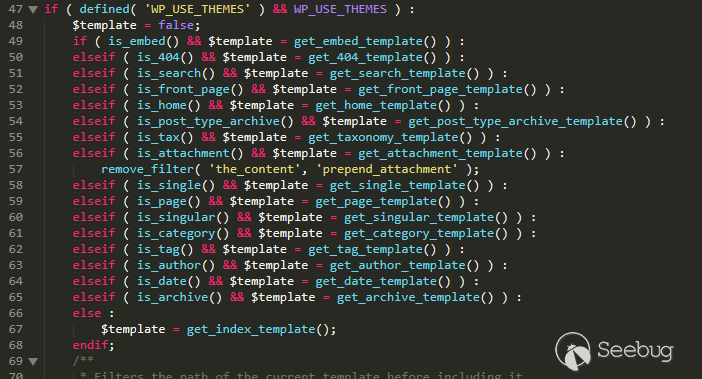
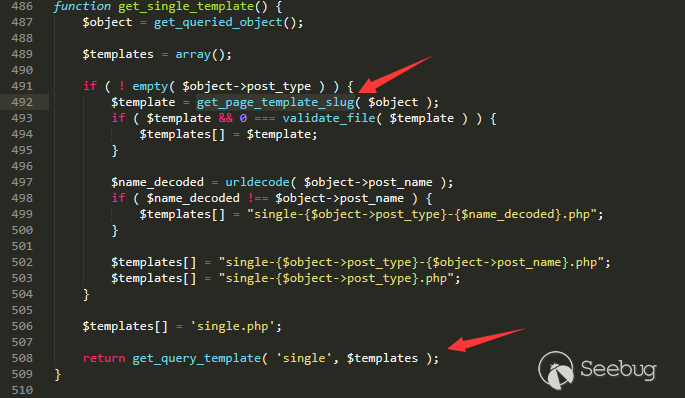
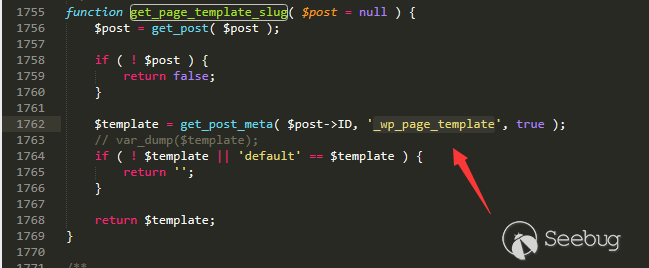
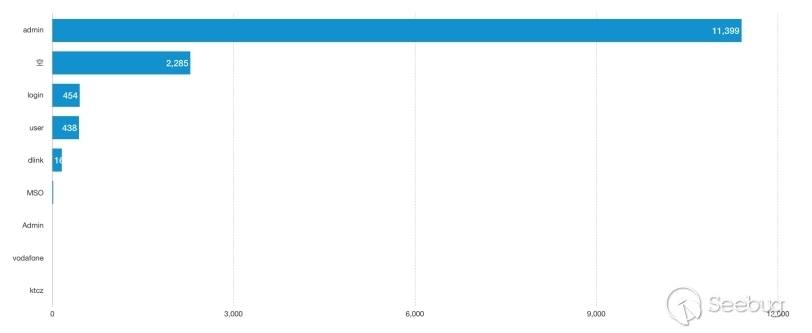
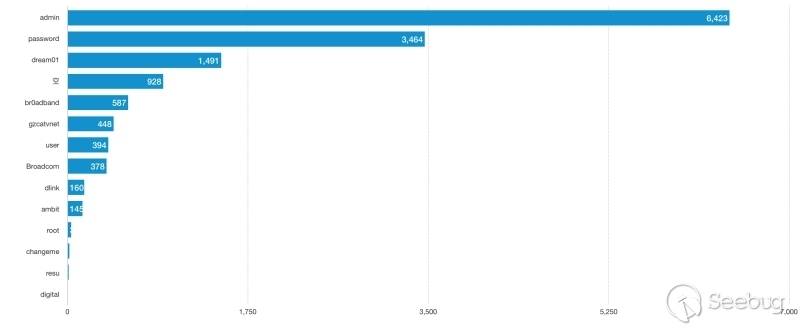
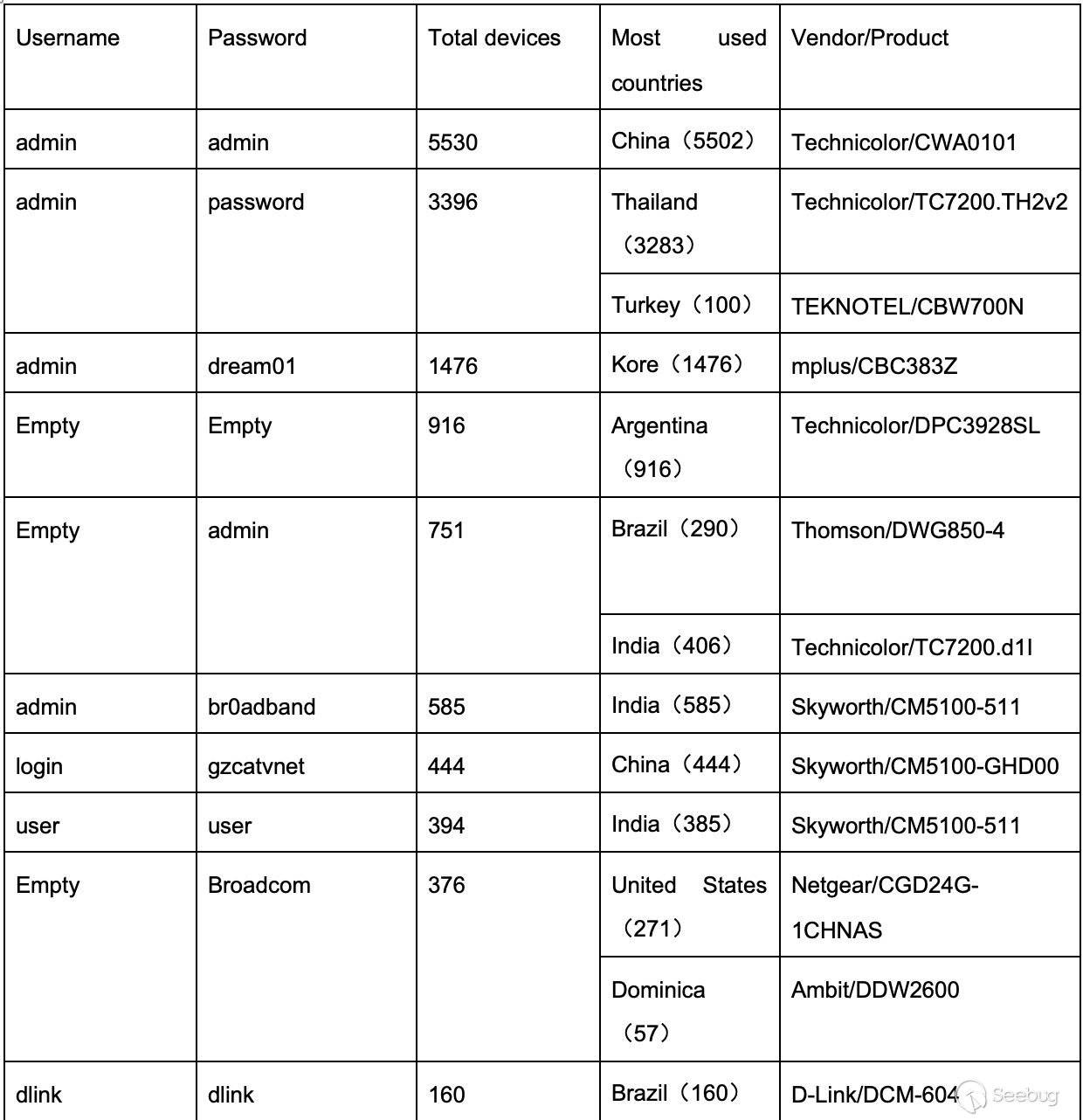
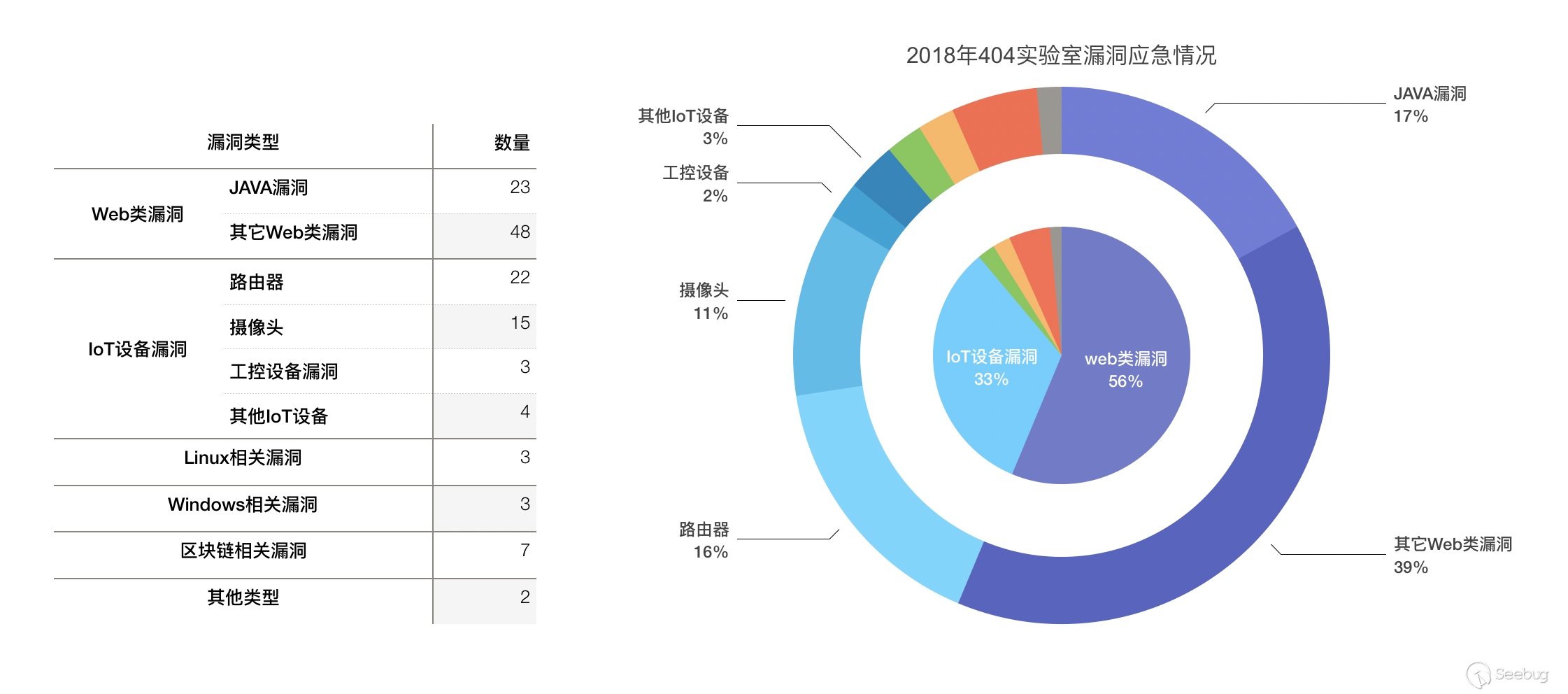
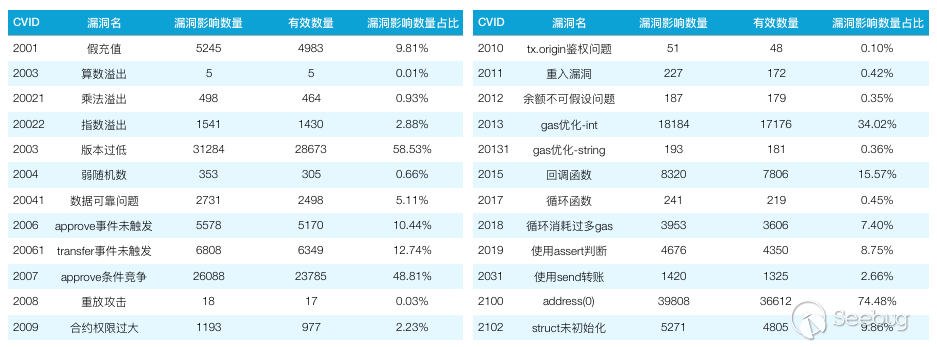
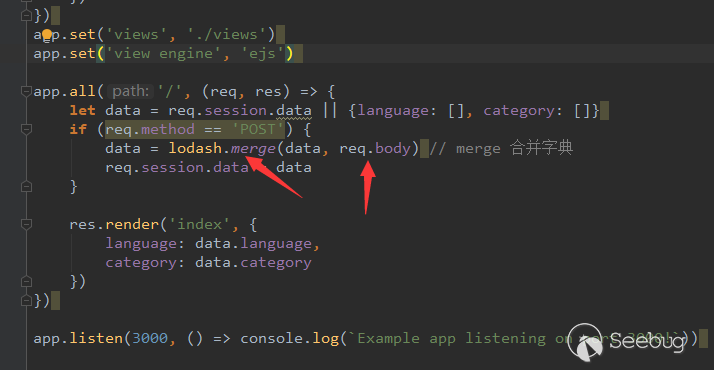
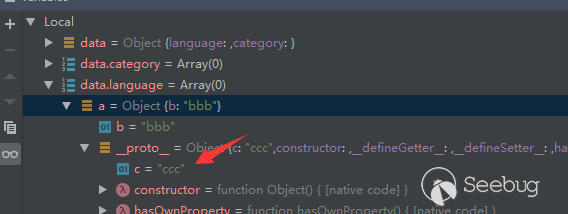
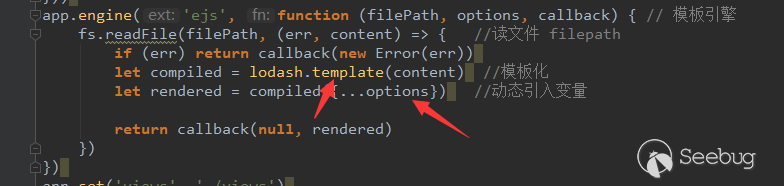
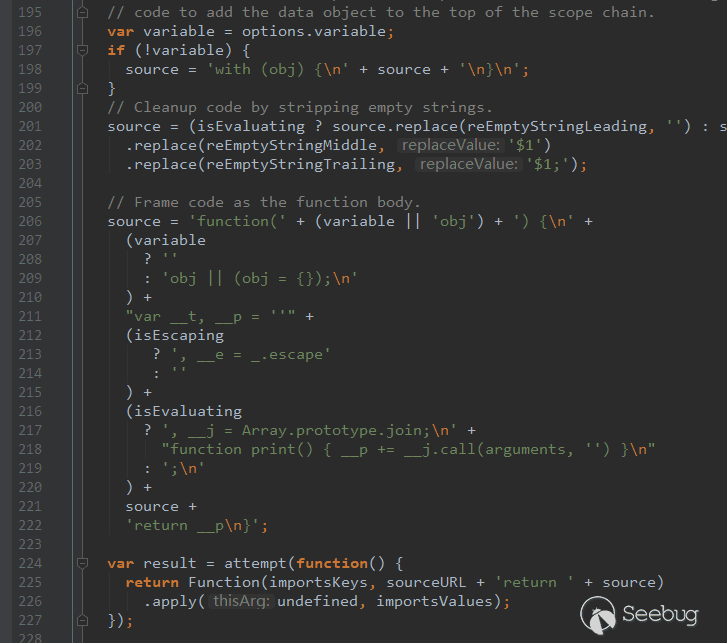
In the Ethereum contract audit CheckList, I divided the 29 issues encountered in Ethereum contract auditing into five major categories, including coding specification issues, design defect issues, coding security issues, coding design issues, and coding security issues. This will help smart contract developers and security workers get started quickly with smart contract security.This CheckList refers to and collates with the research results of the major blockchain security research teams in the completion process. Once imperfections/errors occurred, welcome to submit issues.Because this article is mainly a CheckList, the article will not contain too detailed vulnerability/hazard information, and most of the vulnerability analysis will be mentioned in the scanning report.
1. Coding specification issue
(1) Compiler version
In the contract code, the compiler version should be specified. It is recommended to use the latest compiler version.
Compilers of older versions may cause various known security issues, such as https://paper.seebug.org/631/#44-dividenddistributor
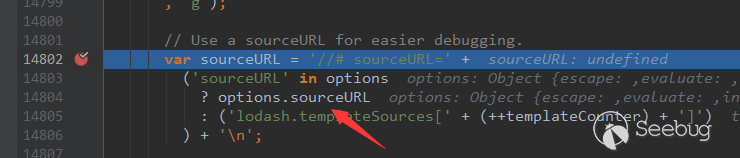
V0.4.23 updates a compiler vulnerability. In this version, if both constructors are used, i.e.,
|
|
contract a { function a() public{ ... } constructor() public{ ... } } |
one of the constructors will be ignored, which only affects v0.4.22. V0.4.25 fixes the uninitialized storage pointer problem mentioned below.
https://etherscan.io/solcbuginfo
(2) Constructor writing issue
The correct constructor should be used for different compiler versions, otherwise the contract owner may change.
In the solidify compiler syntax requirements of versions less than 0.4.22, the contract constructor must be equal to the contract name, and the name is affected by the case, e.g.,
|
|
contract Owned { function Owned() public{ } |
After version 0.4.22, the constructor keyword was introduced as a constructor declaration. But no function is required.
|
|
contract Owned { constructor() public { } |
If you don't follow the corresponding method, the constructor will be compiled into a normal function, which can be called arbitrarily, leading to more serious consequences such as owner permission.
(3) Return standard
Following the ERC20 specification, the transfer and approve functions should return a bool value, and a return value code needs to be added.
|
|
function transfer(address _to, uint256 _value) public returns (bool success) |
The result of transferFrom should be consistent with the result returned by transfer.
(4) Event standard
Follow the ERC20 specification and require the transfer and approve functions to trigger the corresponding event.
|
|
function approve(address _spender, uint256 _value) public returns (bool success){ allowance[msg.sender][_spender] = _value; emit Approval(msg.sender, _spender, _value) return true |
(5) Fake recharge issue
In the transfer function, the judgment of the balance and the transfer amount needs to use the require function to throw an error, otherwise it will judge that the transaction is successful mistakingly.
|
|
function transfer(address _to, uint256 _value) returns (bool success) { if (balances[msg.sender] >= _value && _value > 0) { balances[msg.sender] -= _value; balances[_to] += _value; Transfer(msg.sender, _to, _value); return true; } else { return false; } } |
The above code may cause false recharge.
The correct code is as follows:
|
|
function transfer(address _to, uint256 _value) returns (bool success) { if (balances[msg.sender] >= _value && _value > 0) { balances[msg.sender] -= _value; balances[_to] += _value; Transfer(msg.sender, _to, _value); return true; } else { return false; } } |
2. Design defect issue
(1) Approve authorization function conditional competition
Conditional competition should be avoided in the approve function. Before modifying the allowance, you should change it to 0 first and then to _value.
The reason for this vulnerability is that in order to encourage miners to mine in the underlying miners' agreement, the miners can decide what to pack for themselves. In order to make more profits, the miners generally choose to package the deals with larger gas prices, rather than relying on the order of transactions.
By setting 0, the hazards arising from the conditional competition can be alleviated to some extent. The contract manager can check the log to determine if there is a conditional competition. The greater significance of this fix is to remind users who use the approve function. The operation of this function is irreversible to some extent.
|
|
function approve(address _spender, uint256 _value) public returns (bool success){ allowance[msg.sender][_spender] = _value; return true |
The above code may lead to conditional competition.
So add the following in the approve function:
|
|
require((_value == 0) || (allowance[msg.sender][_spender] == 0)); |
Change the allowance to 0 and then the corresponding number.
(2) Loop dos issue
[1] Loop consumption issue
It is not recommended to use too many loops in contracts.
In Ethereum, each transaction consumes a certain amount of gas, and the actual consumption is determined by the complexity of the transaction. The larger the number of loops, the higher the complexity of the transaction. When the maximum allowable gas consumption is exceeded, the transaction will fail.
Real world event
Simoleon (SIM)
Pandemica
[2] Loop security issue
In the contract, the number of loops should be prevented from being controlled by the user. And the attacker may use an excessive loop to complete the Dos attack.
When a user needs to transfer money to multiple accounts at the same time, we need to traverse the transfer of the target account list, which may lead to DoS attacks.
|
|
function Distribute(address[] _addresses, uint256[] _values) payable returns(bool){ for (uint i = 0; i < _addresses.length; i++) { transfer(_addresses[i], _values[i]); } return true; } |
In the above situation, it is recommended to use withdrawFunds to let the user retrieve their token instead of sending it to the corresponding account. This can reduce the hazard to a certain extent.
If the above code controls a function call, then it can construct a huge loop to consume gas, causing a Dos problem.
3. Coding security issue
(1) Overflow issue
[1] Arithmetic overflow
When calling addition, subtraction, multiplication and division, you should use the safeMath library instead, otherwise it will easily lead to calculation overflow, resulting in inevitable loss.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
pragma solidity ^0.4.18; contract Token { mapping(address => uint) balances; uint public totalSupply; function Token(uint _initialSupply) { balances[msg.sender] = totalSupply = _initialSupply; } function transfer(address _to, uint _value) public returns (bool) { require(balances[msg.sender] - _value >= 0); //Bypass the judgment by underflow. balances[msg.sender] -= _value; balances[_to] += _value; return true; } function balanceOf(address _owner) public constant returns (uint balance) { return balances[_owner]; } } |
balances[msg.sender] - _value >= 0
You can bypass the judgment by underflow.
The usual fix is to use openzeppelin-safeMath, but it may also be limited by judging different variables. However, it is difficult to impose restrictions on multiplication and exponential multiplication.
The correct writing:
|
|
function transfer(address _to, uint256 _amount) public returns (bool success) { require(_to != address(0)); require(_amount <= balances[msg.sender]); balances[msg.sender] = balances[msg.sender].sub(_amount); balances[_to] = balances[_to].add(_amount); emit Transfer(msg.sender, _to, _amount); return true; } |
Real world event
Hexagon
SMT/BEC
[2] Coin/destroy overflow issue
In the coin/destroy function, the upper limit should be set for totalSupply to avoid the increase in malicious coinage events due to vulnerabilities such as arithmetic overflow.
|
|
function TokenERC20( uint256 initialSupply, string tokenName, string tokenSymbol ) public { totalSupply = initialSupply * 10 ** uint256(decimals); balanceOf[msg.sender] = totalSupply; name = tokenName; symbol = tokenSymbol; } |
There is no limit to totalSupply in the above code, which may cause the exponential arithmetic overflow.
The correct writing:
|
|
contract OPL { // Public variables string public name; string public symbol; uint8 public decimals = 18; // 18 decimals bool public adminVer = false; address public owner; uint256 public totalSupply; function OPL() public { totalSupply = 210000000 * 10 ** uint256(decimals); ... } |
Real world event
(2) Reentrancy vulnerability
Avoid using call to trade in smart contracts to avoid reentrancy vulnerabilities.
In the smart contract, call, send, and transfer are provided to trade eth. The biggest difference for call is that there is no limit for gas. The other two, when the gas is not enough, will report out of gas.
There are several characteristics of reentrancy vulnerability.
- Using the call function.
- There is no limit for the call function gas.
- Deducting the balance after the transfer.
- Adding () to execute the fallback
|
|
function withdraw(uint _amount) { require(balances[msg.sender] >= _amount); msg.sender.call.value(_amount)(); balances[msg.sender] -= _amount; } |
The above code is a simple demo of reentrancy vulnerability. A large number of contract tokens are recursively transferred by reentrancy vulnerabilities.
For possible reentrancy issues, use the transfer function to complete the transfer as much as possible, or limit the gas execution of the call. These can effectively reduce the harm.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
contract EtherStore { // initialise the mutex bool reEntrancyMutex = false; uint256 public withdrawalLimit = 1 ether; mapping(address => uint256) public lastWithdrawTime; mapping(address => uint256) public balances; function depositFunds() public payable { balances[msg.sender] += msg.value; } function withdrawFunds (uint256 _weiToWithdraw) public { require(!reEntrancyMutex); require(balances[msg.sender] >= _weiToWithdraw); // limit the withdrawal require(_weiToWithdraw <= withdrawalLimit); // limit the time allowed to withdraw require(now >= lastWithdrawTime[msg.sender] + 1 weeks); balances[msg.sender] -= _weiToWithdraw; lastWithdrawTime[msg.sender] = now; // set the reEntrancy mutex before the external call reEntrancyMutex = true; msg.sender.transfer(_weiToWithdraw); // release the mutex after the external call reEntrancyMutex = false; } } |
The above code is a way to use mutex lock to avoid recursive protection.
Real world event
The Dao
(3) Call injection
When the call function is invoked, you should do strict permission control, or write the function invoked to hardcode directly.
In the design of EVM, if the parameter data of the call is 0xdeadbeef (assumed function name) + 0x0000000000.....01, then it is the invoke function.
Call function injection can lead to token stealing and permission bypass. Private functions and even partially high-privilege functions can be called through call injection.
|
|
addr.call(data); addr.delegatecall(data); addr.callcode(data); |
For example, when the delegatecall function must call another contract within the contract, the keyword library can be used to ensure that the contract is static and indestructible. By forcing the contract to be static, the storage environment can be simple to a certain extent and preventing the attacker from attacking the contract by modifying the state.
Real world events
call injection
(4) Permission control
Different functions in the contract should have reasonable permission settings.
Check whether the functions in the contract use public, private and other keywords correctly for visibility modification. Check whether the contract is correctly defined and use the modifier to restrict access to key functions to avoid unauthorized control.
|
|
function initContract() public { owner = msg.sender; } |
The above code should not be a public function.
Real world event
Parity Multi-sig bug 1
Parity Multi-sig bug 2
Rubixi
(5) Replay attack
If the contract involves the demands for entrusted management, attention should be paid to the non-reusability of verification to avoid replay attacks.
In the asset management system, there are often cases of entrusted management. The principal gives the assets to the trustee for management and pays a certain fee to the trustee. This business scenario is also common in smart contracts.
Here is an example of the transferProxy function, which is used when user1 transfers token to user3 but does not have eth to pay for gas price. In this case, user2 is delegated for payment by calling transferProxy.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
function transferProxy(address _from, address _to, uint256 _value, uint256 _fee, uint8 _v, bytes32 _r, bytes32 _s) public returns (bool){ if(balances[_from] < _fee + _value || _fee > _fee + _value) revert(); uint256 nonce = nonces[_from]; bytes32 h = keccak256(_from,_to,_value,_fee,nonce,address(this)); if(_from != ecrecover(h,_v,_r,_s)) revert(); if(balances[_to] + _value < balances[_to] || balances[msg.sender] + _fee < balances[msg.sender]) revert(); balances[_to] += _value; emit Transfer(_from, _to, _value); balances[msg.sender] += _fee; emit Transfer(_from, msg.sender, _fee); balances[_from] -= _value + _fee; nonces[_from] = nonce + 1; return true; } |
The problem with this function is that the nonce value is predictable. Replay attacks can be performed with other variables unchanged which lead to multiple transfers.
The vulnerability stems from the DEF CON 2018 topics.
Replay Attacks on Ethereum Smart Contracts Replay Attacks on Ethereum Smart Contracts pdf
4. Coding design issue
(1) Address initialization issue
When the address is involved in a function, it is recommended to add the verification of require(_to!=address(0)) to effectively avoid unnecessary loss caused by user misuse or unknown errors.
The address that EVM initializes when compiling the contract code is 0. If the developer initializes an address variable in the code without setting an initial value, or the user does not initialize the address variable upon any mis-operation, and this variable is called in the following code, unnecessary security risks may rise.
This type of check can be used in the simplest way to avoid issues such as unknown errors or short address attacks.
(2) Judgment function issue
When the conditional judgment is involved, the require function instead of the assert function is used. Because assert will cause the remaining gas to be consumed, but they are consistent in other aspects.
It is worth noting that the assert has mandatory consistency. For static variables, assert can be used to avoid some unknown problems, because it will force the termination of the contract and make it invalid. And in some conditions, assert may be more suitable.
(3) Balance judgment issue
Don't assume that the contract is created with a balance of 0 and the transfer can be forced.
Be cautious to write invariants for checking account balances, because an attacker can send wei to any account forcibly, even if the fallback function throws.
The attacker can create a contract with 1wei and then call selfdestruct(victimAddress) to destroy it. This balance is forcibly transferred to the target, and the target contract has no code to execute and cannot be blocked.
It is worth noting that during the packaging process, the attacker can transfer before the contract is created through race condition so that the balance is not 0 when the contract is created.
(4) Transfer function issue
Upon completing a transaction, it is recommended to use transfer instead of send by default.
When the target of the transfer or send function is a contract, the contract's fallback function will be invoked. But if the fallback function failed to execute, transfer will throw an error and automatically roll back, and send will return false. Therefore, you need to judge the return type when using send. Otherwise, the transfer may fail and the balance will decrease.
|
|
function withdraw(uint256 _amount) public { require(balances[msg.sender] >= _amount); balances[msg.sender] -= _amount; etherLeft -= _amount; msg.sender.send(_amount); } |
The above code use the send() function to transfer, because there is no check for the returned value of the send() function.
If msg.sender fail to call the contract account fallback(), send() returns false, which eventually results in a reduction in the account balance with money loss.
(5) External call design issue
For external contracts, pull instead of push is preferred.
In the case of external calls, unpredictable failure happens. In order to avoid unknown loss, the external operations should be changed into user's own disposal.
Error example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
contract auction { address highestBidder; uint highestBid; function bid() payable { if (msg.value < highestBid) throw; if (highestBidder != 0) { if (!highestBidder.send(highestBid)) { // An error may occur. throw; } } highestBidder = msg.sender; highestBid = msg.value; } } |
When a transfer to a party is required, the transfer is changed to define the withdraw function, allowing the user to execute the function by himself and withdraw the balance. This will avoid unknown losses to the greatest extent.
Example code:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
contract auction { address highestBidder; uint highestBid; mapping(address => uint) refunds; function bid() payable external { if (msg.value < highestBid) throw; if (highestBidder != 0) { refunds[highestBidder] += highestBid; // Recorded in the refunds. } highestBidder = msg.sender; highestBid = msg.value; } function withdrawRefund() external { uint refund = refunds[msg.sender]; refunds[msg.sender] = 0; if (!msg.sender.send(refund)) { refunds[msg.sender] = refund; // It can be recovered if the transfer is wrong. } } } |
(6) Error handling
When the contract involves a call or other methods that operates at the base level of the address function, make reasonable error handling.
|
|
address.call() address.callcode() address.delegatecall() address.send() |
If such an operation encounters an error, it will not throw an exception but return false and continue the execution.
|
|
function withdraw(uint256 _amount) public { require(balances[msg.sender] >= _amount); balances[msg.sender] -= _amount; etherLeft -= _amount; msg.sender.send(_amount); } |
The above code does not verify the return value of send. If msg.sender is a contract account, send returns false when the fallback call fails.
So when using the above method, you need to check the return value and make error handling.
|
|
if(!someAddress.send(55)) { // Some failure code } |
https://paper.seebug.org/607/#4-unchecked-return-values-for-low-level-calls
It's worth noting that as a part of the EVM design, the following functions will return True if the contract being called does not exist.
|
|
call、delegatecall、callcode、staticcall |
Before calling such functions, you need to check the validity of the address.
(7) Weak random number issue
The method of generating random numbers on smart contracts requires more considerations.
The Fomo3D contract introduces the block information as a parameter for generating the random number seed in the airdrop reward, which causes the random number seed to be affected only by the contract address and cannot be completely random.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
function airdrop() private view returns(bool) { uint256 seed = uint256(keccak256(abi.encodePacked( (block.timestamp).add (block.difficulty).add ((uint256(keccak256(abi.encodePacked(block.coinbase)))) / (now)).add (block.gaslimit).add ((uint256(keccak256(abi.encodePacked(msg.sender)))) / (now)).add (block.number) ))); if((seed - ((seed / 1000) * 1000)) < airDropTracker_) return(true); else return(false); } |
The above code directly led to the Fomo3D incident causing more than a few thousands eth loss.
So when it comes to such applications in a contract, it is important to consider a more appropriate generation method and a reasonable order of use.
Here is a reasonable random number generation method hash-commit-reveal, i.e., the player submits the action plan and the hash to the back end, which then generates the corresponding hash value as well as the random number to reveal and returns the corresponding random number to commit. In this way, the server can't get the action plan, and the client can't get the random number.
One great implementation code is the random number generation code for dice2win.(https://etherscan.io/address/0xD1CEeeefA68a6aF0A5f6046132D986066c7f9426)
But the biggest problem with hash-commit-reveal is that the server will get all the data in the process briefly after user submits. Maliciously suspending the attack will destroy the fairness to some extent. Detailed analysis can be found in the smart contract game - Dice2win security analysis.
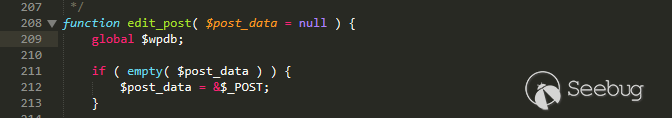
Of course, hash-commit is also a good implementation in some simple scenarios, i.e., the player submits the action plan hash before generating a random number and submitting the action plan.
Real world event
Fomo3D Incident
Last Winner
(8) Variable coverage vulnerability
Avoid the key of the array variable in contract being controlled.
|
|
map[uint256(msg.sender)+x] = blockNum; |
In EVM, arrays are different from other types. As arrays are dynamically sized, array data is calculated as
|
|
address(map_data) = sha3(key)+offset |
The key is the position defined by the map variable, i.e., 1. The offset refers to the offset in the array, e.g., for map[2], the offset is 2.
The address of map[2] is sha3(1)+2. Assuming map[2]=2333, storage[sha3(1)+2]=2333.
This is a problem because offset is controllable so that we can write values to any address of the storage.
This may overwrite the value of any address in the storage, affecting the logic of the code itself, leading to even more serious problems.
For detailed principles, please refer to - 以太坊智能合约 OPCODE 逆向之理论基础篇 - https://paper.seebug.org/739
5. Code hidden danger
(1) Grammatical property issue
Be careful with the rounding down of integer division in smart contracts.
In smart contracts, all integer divisions are rounded down to the nearest integer. For higher precision, a multiplier is needed to increase this number.
If the problem occurs explicitly in the code, the compiler will raise an error and cannot continue compiling. However, if it appears implicitly, the round-down approach will be taken.
Error example:
Correct code:
|
|
uint multiplier = 10; uint x = (5 * multiplier) / 2; |
(2) Data privacy
note that all data in the chain is public.
In the contract, all data including private variables are public. Privacy data cannot be stored on the chain.
(3) Data reliability
In the contract, the timestamp should not be allowed to appear in the code to avoid interference by the miners. Instead, the constant data such as block.height should be used.
|
|
uint someVariable = now + 1; if (now % 2 == 0) { // The now may be controlled by miners. } |
(4) Gas consumption optimization
For some functions and variables that do not involve state changes, you can add constant to avoid gas consumption.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
contract EUXLinkToken is ERC20 { using SafeMath for uint256; address owner = msg.sender; mapping (address => uint256) balances; mapping (address => mapping (address => uint256)) allowed; mapping (address => bool) public blacklist; string public constant name = "xx"; string public constant symbol = "xxx"; uint public constant decimals = 8; uint256 public totalSupply = 1000000000e8; uint256 public totalDistributed = 200000000e8; uint256 public totalPurchase = 200000000e8; uint256 public totalRemaining = totalSupply.sub(totalDistributed).sub(totalPurchase); uint256 public value = 5000e8; uint256 public purchaseCardinal = 5000000e8; uint256 public minPurchase = 0.001e18; uint256 public maxPurchase = 10e18; |
(5) Contract users
In the contract, we should try to consider the situation when the trading target is the contract and avoid the various malicious uses incurred thereby.
|
|
contract Auction{ address public currentLeader; uint256 public hidghestBid; function bid() public payable { require(msg.value > highestBid); require(currentLeader.send(highestBid)); currentLeader = msg.sender; highestBid = currentLeader; } } |
The above contract is a typical case when the contract is not considered as a user. This is a simple bidding code to compete for the king. When the trade ether is bigger than the highestBid in the contract, the current user will become the current "king" of the contract, and his trading amount will become the new highestBid.
|
|
contract Attack { function () { revert(); } function Attack(address _target) payable { _target.call.value(msg.value)(bytes4(keccak256("bid()"))); } } |
However, when a new user tries to become the new "king" and the code executes to require(currentLeader.send(highestBid));, the fallback function in the contract is triggered. If the attacker adds a revert() function to the fallback function, the transaction will return false and the transaction will never be completed. Then the current contract will always be the current "king" of the contract.
(6) Log records
Key events should have an Event record. In order to facilitate operation, maintenance and monitoring, in addition to functions such as transfer and authorization, other operations also need to add detailed event records such as administrator permission transfer and other special main functions.
|
|
function transferOwnership(address newOwner) onlyOwner public { owner = newOwner; emit OwnershipTransferred(owner, newowner); } |
(7) Fallback function
Define the Fallback function in the contract and make the Fallback function as simple as possible.
The fallback will be called when there is a problem with the execution of the contract (if there is no matching function). When the send or transfer function is called, only 2300 gas is used to execute the fallback function after the failure. The 2300 gas only allows a set of bytecode instructions to be executed and needs to be carefully written to avoid the use of gas.
Some examples:
|
|
function() payable { LogDepositReceived(msg.sender); } function() public payable{ revert();}; |
(8) Owner permission issue
Avoiding the owner permission is too large.
For contract owner permissions that are too large, the owner can freely modify various data in the contract, including modification rules, arbitrary transfer, and any coinage. Once a safety issue occurs, it may lead to serious results.
Regarding the owner permission issue, several requirements should be followed:
- After the contract is created, no one can change the contract rules, including the size of the rule parameters.
- Only the owner is allowed to withdraw the balance from the contract
(9) User authentication issue
Don't use tx.origin for authentication in the contract.
Tx.origin represents the initial address. If user a invokes contract c through contract b, for contract c, tx.origin is user a, and msg.sender is contract b. This represents a possible phishing attack, which is extremely dangerous for authentication.
Here's an example:
|
|
pragma solidity >0.4.24; // THIS CONTRACT CONTAINS A BUG - DO NOT USE contract TxUserWallet { address owner; constructor() public { owner = msg.sender; } function transferTo(address dest, uint amount) public { require(tx.origin == owner); dest.transfer(amount); } } |
We can construct an attack contract:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
pragma solidity >0.4.24; interface TxUserWallet { function transferTo(address dest, uint amount) external; } contract TxAttackWallet { address owner; constructor() public { owner = msg.sender; } function() external { TxUserWallet(msg.sender).transferTo(owner, msg.sender.balance); } } |
When the user is spoofed and invokes the attack contract, it will bypass the authentication directly and transfer the account successfully. Here you should use msg.sender to do permission judgment.
https://solidity.readthedocs.io/en/develop/security-considerations.html#tx-origin
(10) Race condition issue
Try to avoid relying on the order of transactions in the contract.
In smart contracts, there is often a reliance on the order of transactions. Such as the rule of occupying a hill to act as a lord or the last winner rule. These are rules that are designed because of the strong dependence on the order of transactions. But the bottom rule of Ethernet is based on the law of maximum interests of miners. Within a certain degree of limit, as long as the attackers pay enough costs, he can control the order of the transactions to a certain extent. Developers should avoid this problem.
Real world event
Fomo3D Incident
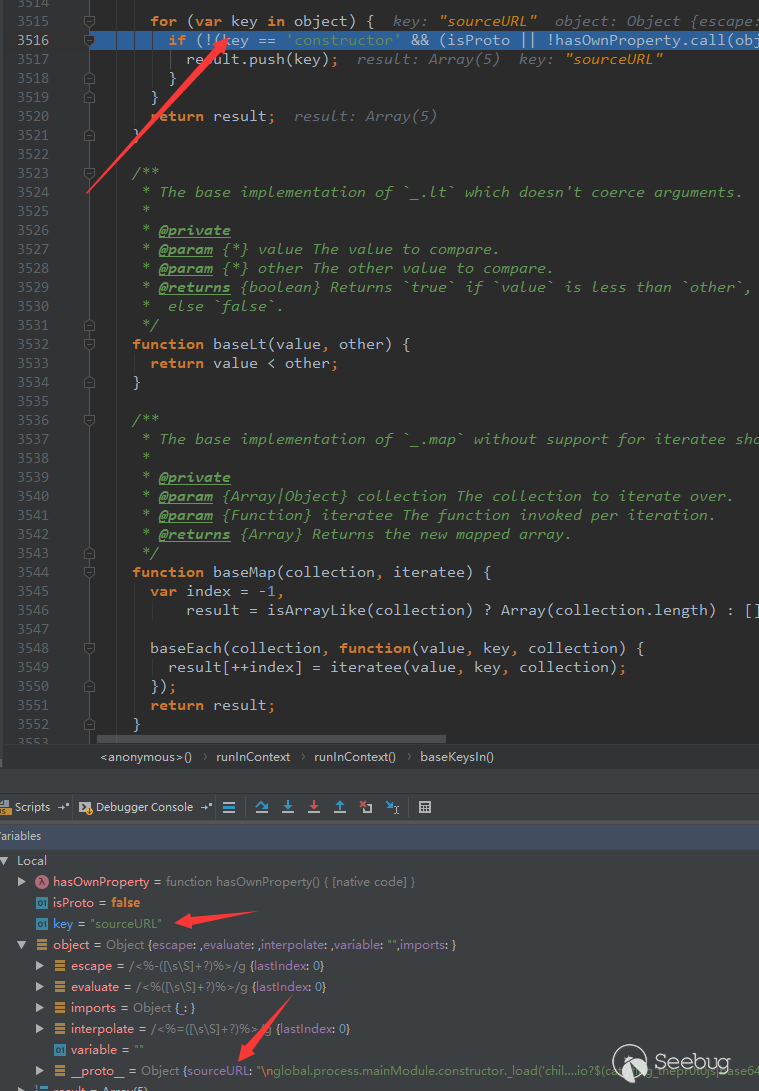
(11) Uninitialized storage pointer
Avoiding initializing struct variables in functions.
A special data structure is allowed to be a struct structure in solidity, and local variables in the function are stored by default using storage or memory.
Storage and memory are two different concepts. Solidity allows pointers to point to an uninitialized reference, and uninitialized local storage causes variables to point to other stored variables. This can lead to variable coverage and even more serious consequences.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
pragma solidity ^0.4.0; contract Test { address public owner; address public a; struct Seed { address x; uint256 y; } function Test() { owner = msg.sender; a = 0x1111111111111111111111111111111111111111; } function fake_foo(uint256 n) public { Seed s; s.x = msg.sender; s.y = n; } } |
After the above code is compiled, s.x and s.y will point incorrectly to owner and a.
After the attacker executes fake_foo, the owner will be changed to himself.
The above issue was fixed in the latest version of 0.4.25.
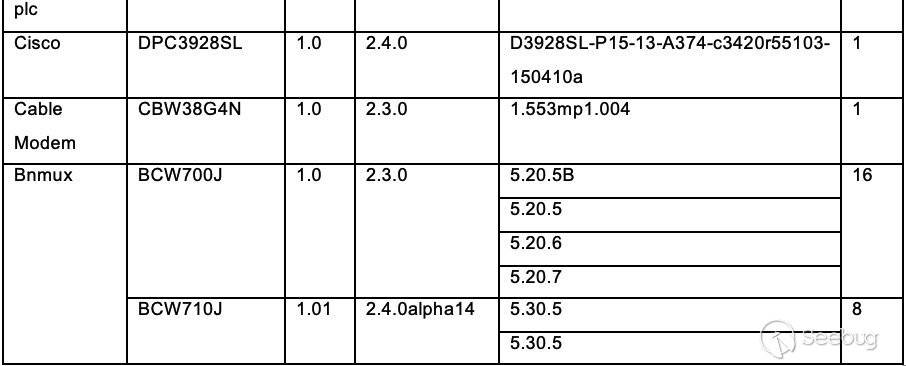
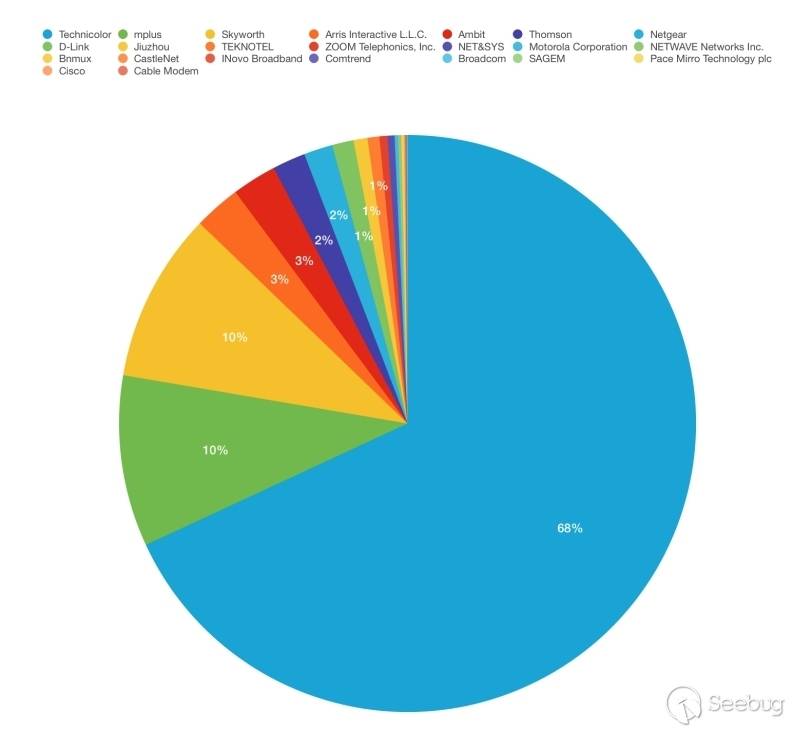
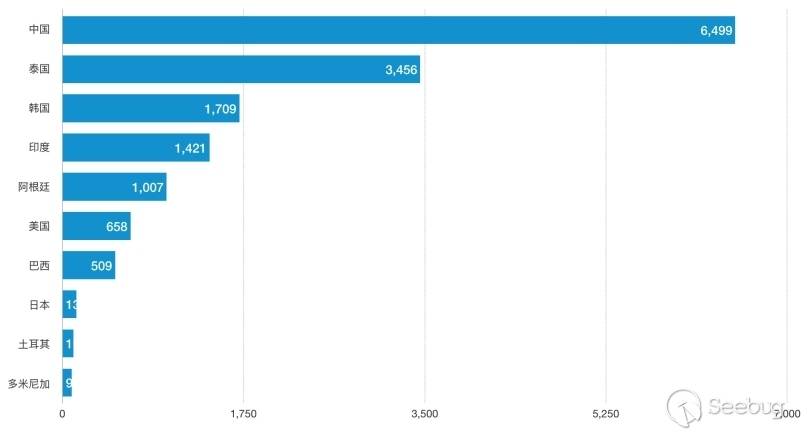
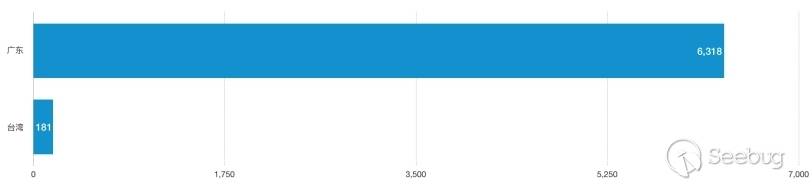
CheckList audit reports
REF
 本文由 Seebug Paper 发布,如需转载请注明来源。本文地址:https://paper.seebug.org/754/
本文由 Seebug Paper 发布,如需转载请注明来源。本文地址:https://paper.seebug.org/754/